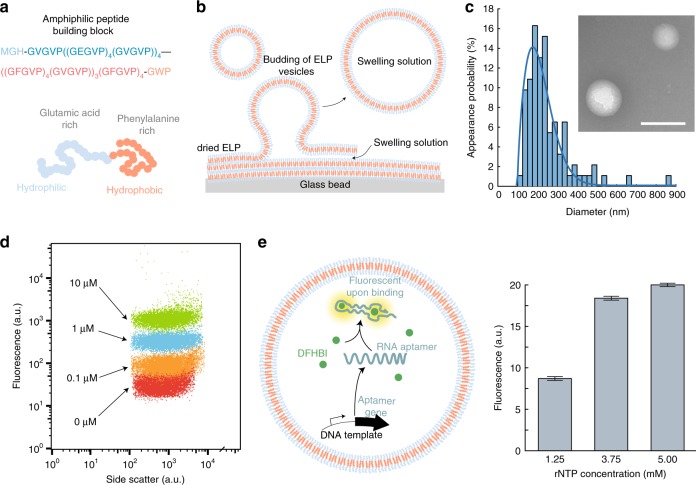
Fig. 1.
ELP vesicle formation and transcription. a The peptide building block is an amphiphilic ELP with a hydrophilic glutamic acid-rich domain and a hydrophobic phenylalanine-rich domain. b For vesicle formation dried ELPs are rehydrated from glass beads. c Size distribution of the produced vesicles obtained from TEM measurements with diameter of 176 nm. The data are described using a Weibull probability distribution (solid line). The inset shows a typical TEM image. Scale bar: 200 nm. d Co-localization of fluorescently labeled DNA (with indicated concentrations) into the vesicles measured by flow cytometry. e Left: Illustration of the transcription of an RNA aptamer inside of an ELP vesicle. The aptamer binds to DFHBI, which then fluoresces. Right: Plateau value means of the DFHBI fluorescence after 50 min of transcription for various rNTP concentrations. The given error bars indicate the sample standard deviation of the measured plateau values