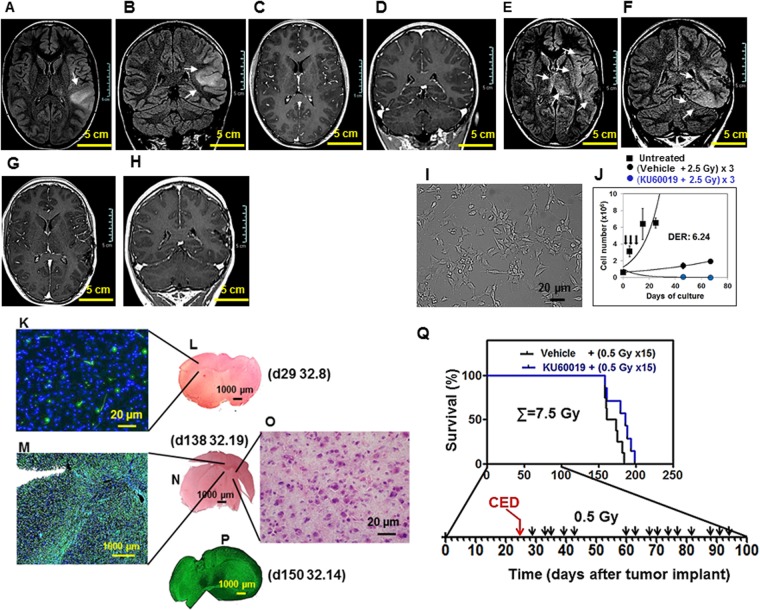
Figure 7.
The GIC-driven pediatric 239/12 tumor and its radiosensitization by KU60019. (A–D) Patient’s tumor at admission: axial and coronal brain MRI FLAIR images demonstrate a diffusely infiltrating lesion (arrows, A,B) involving the cortical-subcortical region of the left temporo-parietal junction without contrast enhancement (C,D, post-contrast T1-weighted images). (E–H) Patient’s tumor at progression: axial and coronal FLAIR images shows subtle diffuse infiltration of the brain parenchyma adjacent to the surgical bed and extending to the ipsilateral insular and temporal region with concomitant bi-thalamic involvement (arrows, E,F). Post-contrast T1-weighted images (G,H) do not show blood brain barrier disruption or necrotic areas. (I) GIC i: the GIC component of the tumor was isolated immediately after surgery. Under matrigel-coating and serum-free conditions, the cells grew and layered onto a monolayer, maintaining intact self-renewal capacity. (J) GIC ii: the 239/12 GIC could be effectively radiosensitized in vitro by exposure to 1 µM KU60019 30 min prior to irradiation with three 2.5 Gy IR fractions [blue versus black circles; reproduced from13, with permission]. The in vitro growth pattern of unirradiated cells is indicated by black squares. (K–O) Orthotopic tumor. 2 × 105 239/12 serum-free grown GIC were stereotactically injected into the left corpus striatum of NOD SCID mice. Immunostaining with an antibody directed against human nestin revealed at both d29 (K) and d138-150 (M,P) an infiltrating, gliomatosis-like, growth pattern of the orthotopic tumor exerting limited mass effect and reflecting the characteristics of the clinical tumor (A–H). Staining with hematoxylin/eosin of brain tissue could reveal the presence of this highly infiltrating tumor only at late times of tumor development and elevated magnification (d138; N,O). Mouse ID numbers 32.8, 32.19 and 32.14 are indicated for the sake of reference with the days (d) of tumor development. (Q) Beneficial effect on animal survival after RT hyperfractionation in the presence of KU60019. At d25 of tumor development, animals were i.c.-injected by CED in the surgery room with 12.5 µl of 250 µM KU60019 (blue) or vehicle (ethanol in 0.9% NaCl - black) followed by irradiation with 15 fractions of 0.5 Gy IR delivered to the head of mice 2–4 days apart from d29 until d94 (total dose delivered: 7.5 Gy). Kaplan-Meier survival curves are shown. Median survival of KU60019-treated animals was increased (186 vs 167 days; ratio: 0.8978; 95% CI of ratio: 0.5352 to 1.260; P: 0.0891) with respect to controls.