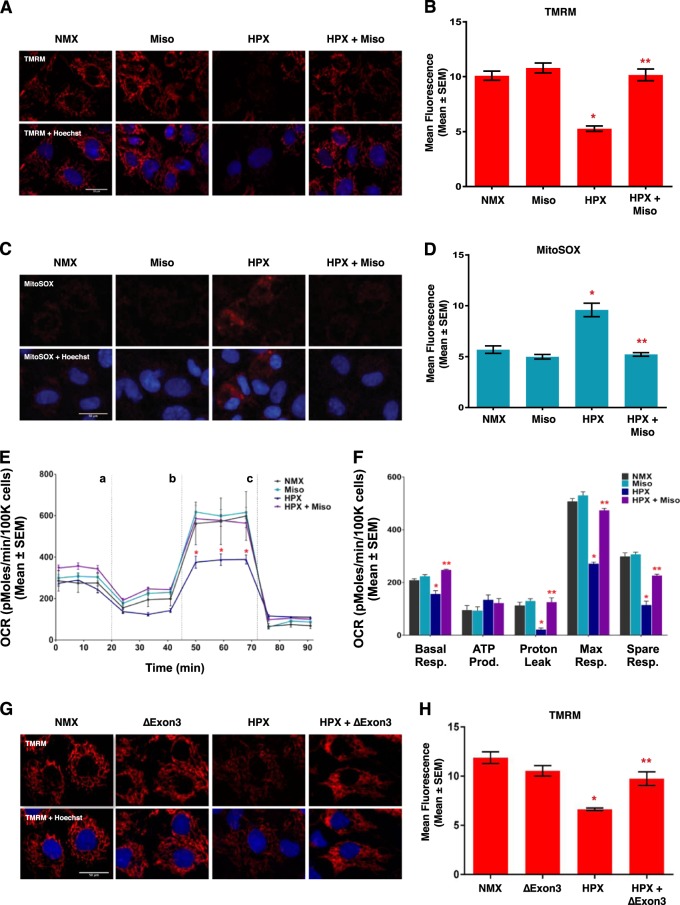
Fig. 4. Misoprostol opposes hypoxia-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in primary ventricular neonatal cardiomyocytes.
a Primary ventricular neonatal cardiomyocytes (PVNM) cells were treated with 10 μM misoprostol (Miso) ± 10% O2 (HPX) for 48 h. Cells were stained with TMRM (red) and Hoechst (blue) and imaged by standard fluorescence microscopy. b Quantification of TMRM in a, red fluorescent signal was normalized to cell area and quantified in 10 random fields. c PVNM cells were treated as described in a. Cells were stained with MitoSOX (red) to evaluate mitochondrial superoxides and Hoechst (blue) and imaged by standard fluorescence microscopy. d Quantification of (c), red fluorescent signal was normalized to cell area and quantified in 10 random fields. e Oxygen consumption rate (OCR) was evaluated on a Seahorse XF-24 in PVNM. To evaluate mitochondrial function, wells were injected with oligomycin (1 μM) (a), FCCP (1 μM) (b), and antimycin A (1 μM) and rotenone (1 μM) (c). f Calculated respiration rates from (e). g PVNM cells were transduced with Bnip3ΔExon3 ± 10% O2 (HPX) for 48 h. Cells were stained with TMRM (red) and Hoechst (blue) and imaged by standard fluorescence microscopy. h Quantification of g, red fluorescent signal was normalized to cell area and quantified in 10 random fields. Data are represented as mean ± S.E.M. *P < 0.05 compared with control, while **P < 0.05 compared with hypoxia treatment, determined by 1-way ANOVA