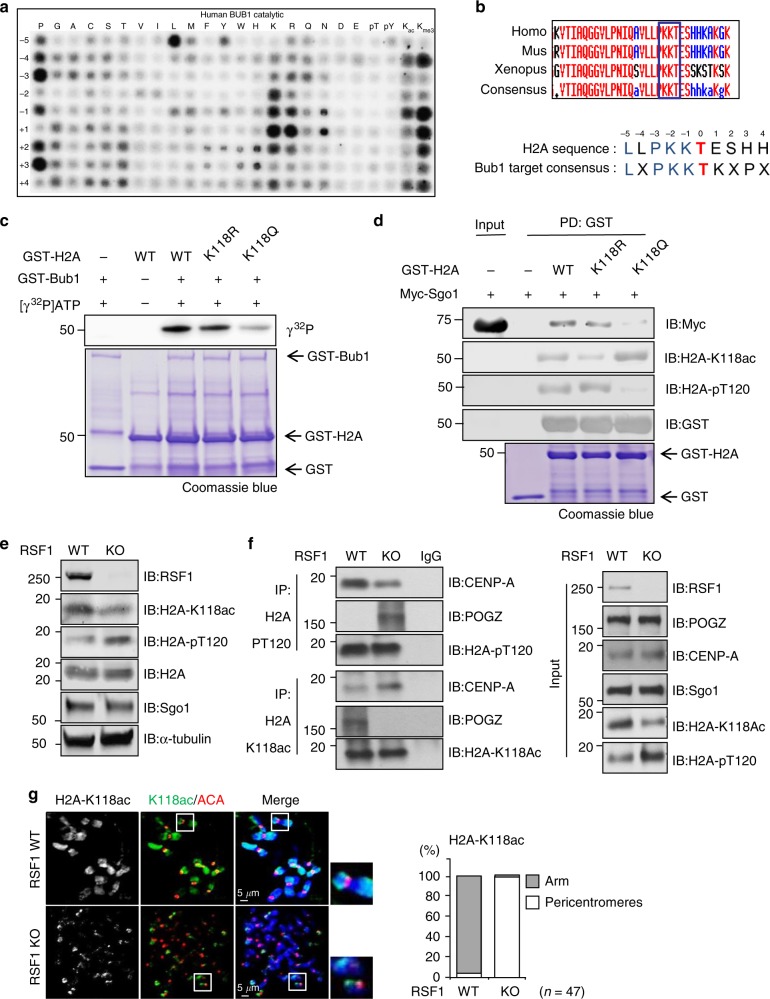
Fig. 2.
Acetylation of H2A-K118 suppresses H2A-T120 phosphorylation and Sgo1 deposition. a Individual in vitro kinase assays were carried out with recombinant GST-Bub1 kinase and a positional scanning peptide library consisting of 189 biotinylated substrate peptides. b Alignment of vertebrate H2A sequence with the conserved Bub1 consensus motif. c In vitro kinase assay: recombinant GST-H2A proteins purified from bacteria were incubated with the GST-Bub1 at 30 °C for 30 min in the presence of γ32P-ATP. Incorporation of 32P into H2A protein was visualized by autoradiography. Coomassie blue staining demonstrated equal protein loading. d Recombinant GST-H2A proteins were incubated with Myc-tagged Sgo1 expressing mitotic whole cell lysates for 12 h at 4 °C and subjected to immunoblotting. e RSF1 WT or KO HeLa cells were treated with paclitaxel for 16 h. Mitotic cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting. f Mitotic RSF1 WT or KO HeLa cell lysates were immunoprecipitated using anti-H2A-pT120 or anti-H2A-K118ac antibodies. The inputs and immunoprecipitates were analyzed by western blot using anti-CENP-A or anti-POGZ. CENP-A or POGZ proteins are specifically localized on the mitotic centromeres and chromosome arms, respectively. g Mitotic HeLa cells were stained with DAPI and H2A-K118ac (green), ACA (red), and DAPI (blue) antibodies. The percentages of cells exhibiting the chromosome arm or centromeric localizations of H2A-K118 acetylation levels are shown. Scale bar, 5 μm