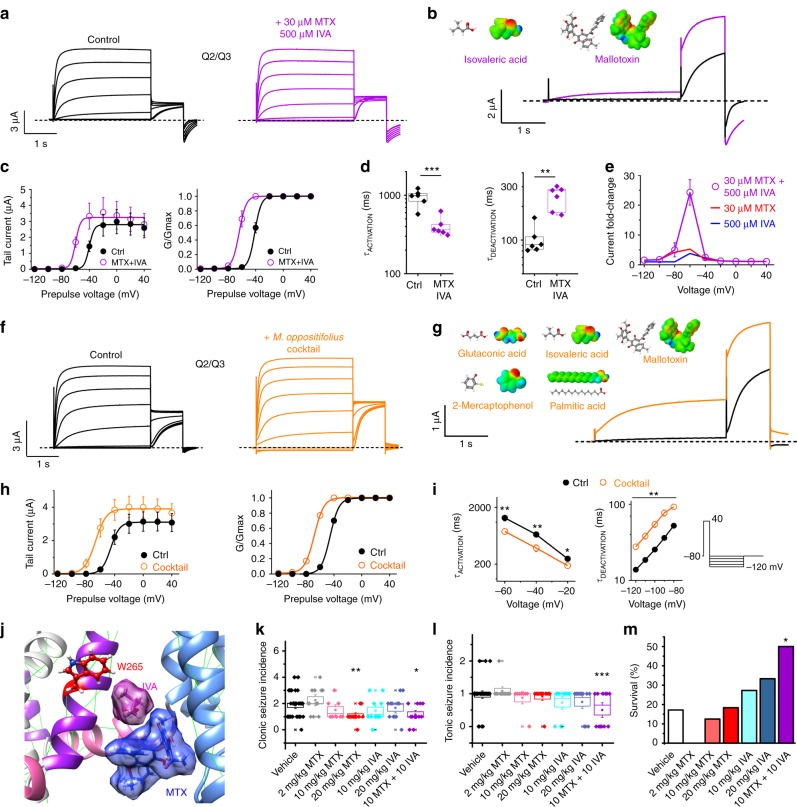
Fig. 6.
MTX and IVA synergize to activate KCNQ2/3 and protect against seizures. a Averaged traces showing effects of IVA and MTX on KCNQ2/3 (n = 5). Voltage protocol as in Fig. 1d. b Effects at −60 mV highlighted, from traces as in a. c Mean tail current and G/Gmax from traces as in a (n = 5). d Mean effect of IVA (500 µM) + MTX (30 µM) on KCNQ2/3 activation at +40 mV and deactivation at −80 mV (n = 5). ***p = 0.0009; **p = 0.001. e Mean KCNQ2/3 current fold-increase versus voltage induced by IVA and MTX alone (from Figs. 2 and 4) or in combination (from traces as in a); n = 4–9. f Averaged traces showing effects of leaf extract cocktail (compounds shown in g) on KCNQ2/3 (n = 7). Voltage protocol as in Fig. 1d. g Effects at −60 mV highlighted, from traces as in f. h Mean tail current and G/Gmax from traces as in f (n = 7). i Mean effect of leaf extract cocktail on rates of KCNQ2/3 activation (left) and deactivation (center; voltage protocol on right) (n = 7). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01. j Binding position of IVA and MTX in KCNQ3 predicted by SwissDock using a chimeric KCNQ1–KCNQ3 structure model. k–m Effects of vehicle (n = 35) compared to IVA and MTX alone or in combination (n = 11–12) on k clonic seizure incidence, l tonic seizure incidence, and m seizure assay survival in a mouse PTZ chemoconvulsant assay. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. Survival statistical analysis by chi-squared, all others by one-way ANOVA. All error bars indicate SEM. All box and whisker plots: box range, 25–75%, coefficient 1; whisker range, 5–95%, coefficient 1.5