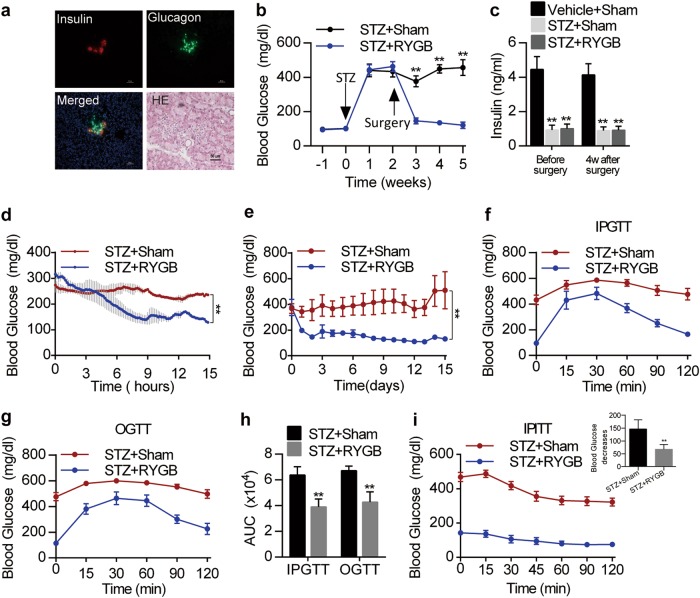
Fig. 6. Effect of RYGB on glucose homeostasis in islet-disrupted rats.
a Immunofluorescence staining for insulin and glucagon and HE staining of pancreatic islets in STZ-treated rats. Scale bar represents 50 μm. b Weekly fasting blood glucose levels of the indicated groups from -1 to 5 weeks (n = 7). c Plasma insulin levels in sham or RYGB treated vehicle or STZ injected rats before and 4 weeks after surgery (n = 7). d Ambulatory blood glucose levels in sham- or RYGB-treated STZ injected rats within 15 h after surgery (n = 2). e Mean 24-h ambulatory blood glucose levels sham- or RYGB-treated STZ injected rats within 15 days after surgery (n = 2). f–h Results of the IPGTT (f) and OGTT (g) for sham- or RYGB-treated STZ injected rats; corresponding AUC values are shown in H (n = 4–5). i IPITT for sham- or RYGB-treated STZ injected rats. Values are shown as the mean ± s.e.m. Significance was calculated using repeated-measures analysis (b) and two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc analysis (c–e), and two-tailed unpaired t-test ( h and i). *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 compared with the surgery group in b and d–e, compared with the sham group in h and compared with the vehicle + sham group in c