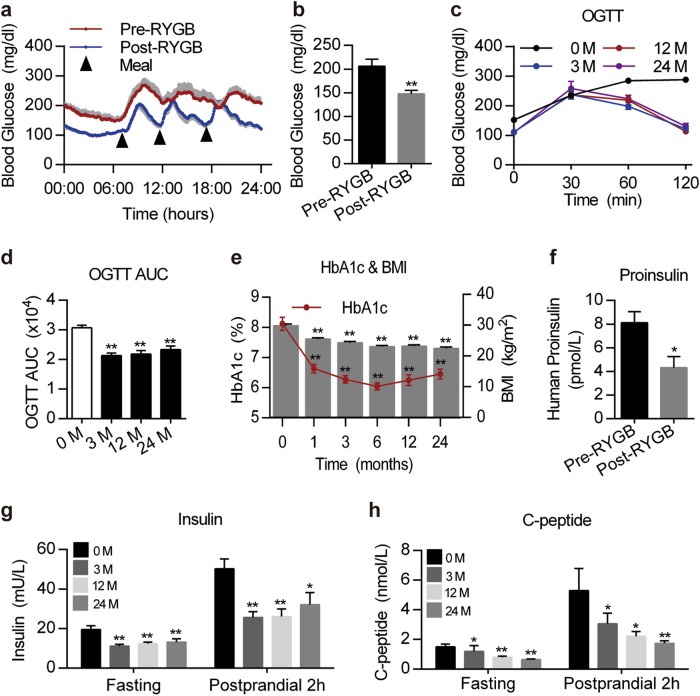
Fig. 7. RYGB remits hyperglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes.
a, b 24-h dynamic and mean blood glucose values in patients pre- and post-RYGB surgery (n = 9 pre-RYGB and 15 post-RYGB). c, d OGTT results for patients at 0, 3, 12 and 24 months after surgery (n = 25–83). e Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) levels and body mass index (BMI) at different time points for T2DM patients who underwent RYGB surgery (n = 23–87). f Serum proinsulin levels of patients before and after surgery (n = 9–12). g Plasma insulin levels and AUC values of the insulin release test at different time points for T2DM patients who underwent RYGB surgery (0 M (pre-RYGB); 3 M (3 months); 12 M (12 months); 24 M (24 months), n = 25–70). h Serum C-peptide levels of T2DM patients at the indicated times before and after RYGB upon glucose stimulation for 2 h (n = 24–78). Values are shown as the mean ± s.e.m. The significance was calculated using a two-tailed unpaired t-test (b), Mann–Whitney nonparametric U test (f), and repeated-measures analysis (d, g–h). *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 compared with the pre-RYGB values