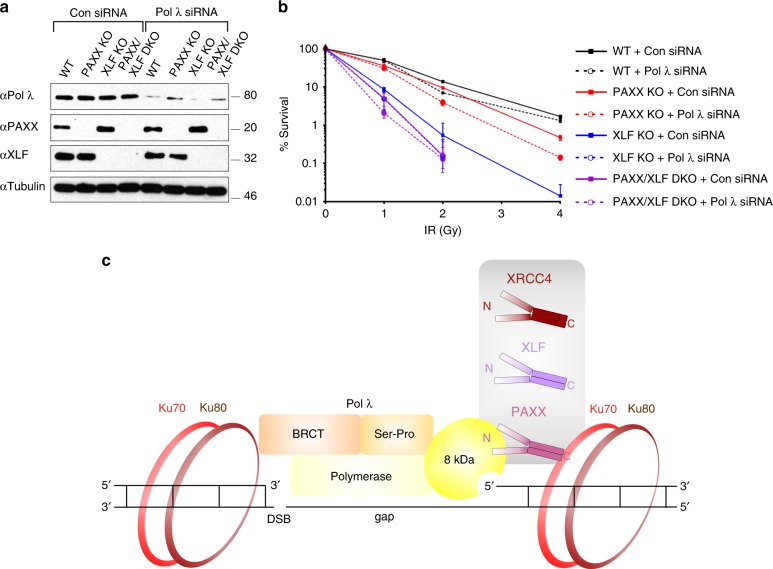
Fig. 10.
Pol λ, PAXX and XLF function in common and parallel pathways. a Immunoblot analysis of control- or Pol λ siRNA-depleted U2OS PAXX KO, XLF KO and PAXX/XLF DKO cells. WCL were resolved by SDS-PAGE and indicated proteins detected by immunoblotting. b Clonogenic survival assays following IR (0-4 Gy) for U2OS WT, -PAXX KO, -XLF KO and -PAXX/XLF DKO cells with or without depletion of Pol λ Mean and SD from three independent experiments are shown. Statistical analysis was performed using a two-tailed paired t-test to compare cells incubated with Pol λ siRNA with control siRNA: 1 Gy - WT p = 0.91, PAXX KO p = 0.38, XLF KO p = 0.10, PAXX/XLF DKO p = 0.10; 2 Gy - WT p = 0.0003, PAXX KO p = 0.0007, XLF KO p = 0.36, PAXX/XLF DKO p = 0.82; 4 Gy - WT = 0.02, PAXX KO = 0.002, XLF KO p = not determined, PAXX/XLF DKO p = not determined. c Cartoon showing a model for regulation of Pol λ by XRCC4 family proteins. At DSBs that are positioned proximal to a Pol λ substrate gap XRCC4 family proteins strongly interact with Ku heterodimers via their C-terminal regions; their head domains promote gap filling synthesis activity via comparatively weakly binding to the 8 kDa domain of Pol λ, which interacts with the 5′ end of the gap. Pol λ strongly interacts with Ku heterodimers via its N-terminal BRCT domain