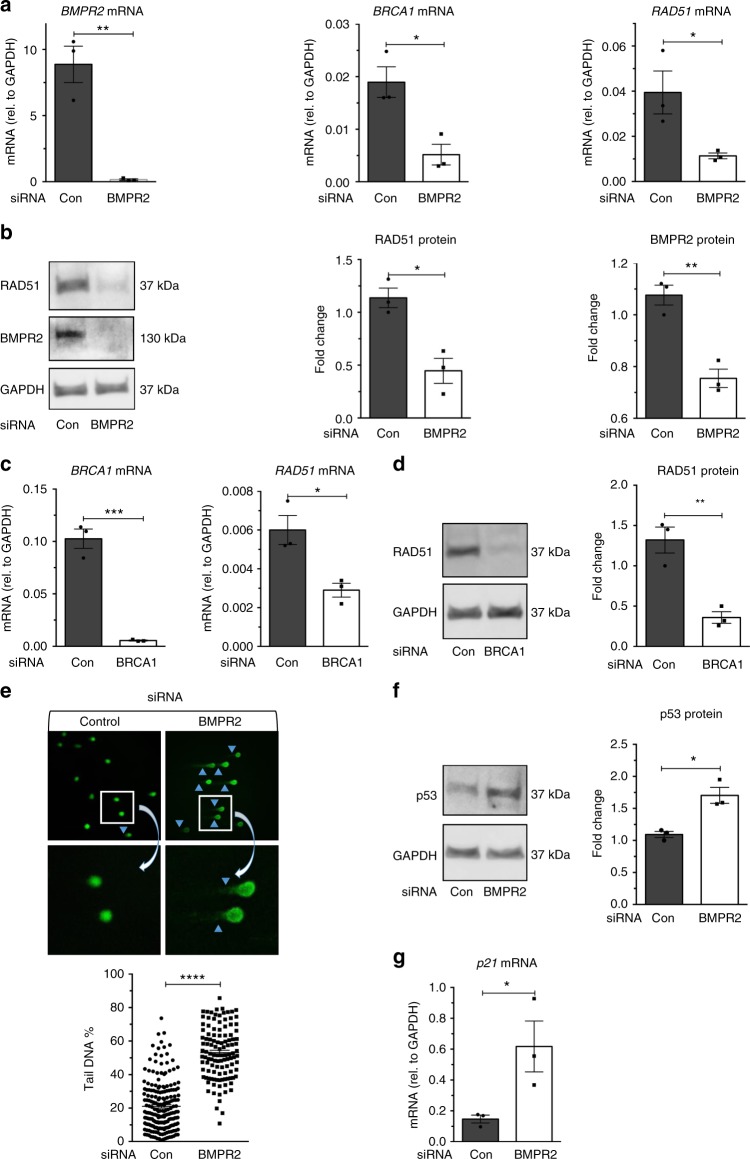
Fig. 1.
Ablation of BMPR2 results in a reduction of RAD51 and promotes DNA damage. a The amount of BMPR2, BRCA1, and RAD51 mRNA relative to GAPDH mRNA was measured 48 h after control (Con) or BMPR2 siRNA transfection initiations using quantitative PCR analysis (n = 3). b The amount of RAD51, BMPR2, and GAPDH (loading control) protein in Con or BMPR2 siRNA-transfected pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells (PMVECs). GAPDH was used for normalization. Representative image and the quantitations of three independent experiments are shown (n = 3). c The level of BRCA1 and RAD51 mRNA relative to GAPDH mRNA in Con or BRCA1 siRNA-transfected PMVECs (n = 3). d RAD51 and GAPDH (loading control) protein amount in Con or BRCA1 siRNA-transfected PMVECs were analyzed. Representative image and the quantitation of three independent experiments are shown (n = 3). e DNA damage of control (Con) or BMPR2 siRNA-transfected PMVECs were analyzed 48 h after siRNA transfection initiation using alkaline single-cell gel electrophoresis (alkaline comet assay). The fraction (%) of cells with DNA damage (arrow heads) was analyzed by ImageJ software. Representative images of alkaline comet assay and the quantitation of 116–204 cells are shown. f p53 protein amount (n = 3) and g p21 mRNA expression (n = 3) in Con or BMPR2 siRNA-transfected PMVECs was examined. GAPDH was used for normalization. Bars represent mean ± SEM from three different experiments per conditions in (a–g). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001 versus respective control. Unpaired two-tailed t-test was used in (a–g)