Fig. 5.
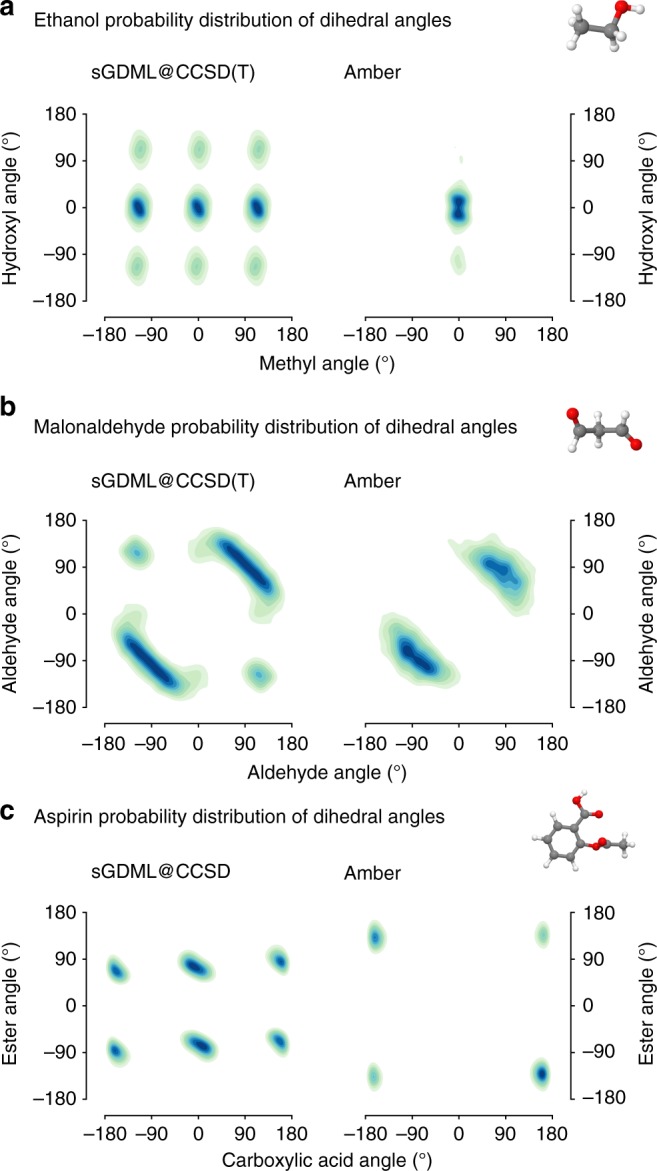
Accuracy of the sGDML model in comparison to a traditional force field. We contrast the dihedral angle probability distributions of ethanol, malonaldehyde, and aspirin obtained from classical MD simulations at 300 K with sGDML (left column) vs. the AMBER70 (right column) force field. The ethanol simulations were carried out at constant energy (NVE), whereas a constant temperature (NVT) was used for malonaldehyde and aspirin. a Ethanol: the coupling between the hydroxyl and methyl rotor is absent in AMBER. Moreover, the probability distribution shows an unphysical harmonic sampling at room temperature, revealing the oversimplified harmonic description of bonded interactions in that force field. b, c Malonaldehyde and aspirin: the formulation of the AMBER force field is dominated by Coulomb interactions, which can lead an incomplete description of the PES and even spurious global minima in the case of aspirin. The length of the simulations was 0.5 ns
