Fig. 2.
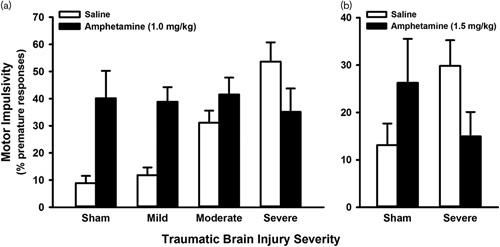
Differential effects of amphetamine challenge on motor impulsivity after traumatic brain injury (TBI). (a) High-dose amphetamine significantly reduced impulsivity on the five-choice serial reaction time task, but only for animals with a severe focal TBI (P=0.002) (adapted with permission from Vonder Haar et al., 2016, copyright 2016 American Chemical Society). (b); High-dose amphetamine significantly reduced impulsivity on the rodent gambling task in animals with a severe focal TBI (P=0.011) (Ozga JE, O'Hearn CM, Shaver TK, Lake AD, Vonder Haar C, unpublished data). Adaptations are themselves works protected by copyright. So in order to publish this adaptation, authorization must be obtained both from the owner of the copyright in the original work and from the owner of copyright in the translation or adaptation.
