Figure 2.
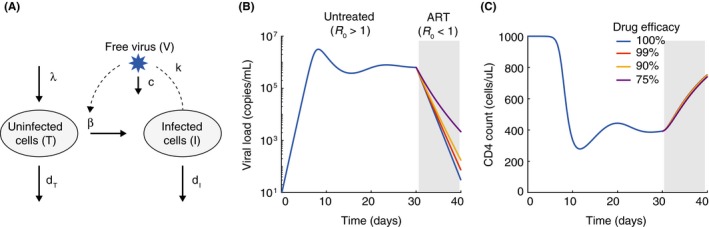
The basic viral dynamics model for HIV. (A) Diagram of the variables and reactions tracked by the model, as described in the text. B‐C) Example time‐course of viral loads (B) and CD4 counts (C) from the model, starting from initial infection, for 30 days before 10 days of antiretroviral therapy. We assume that therapy changes β. As long as therapy leads to R 0 < 1, the decay slope is not very sensitive to the treatment efficacy. Parameters for the model were: λ = 100 cells/uL/d, β = 3× 10−7/(virus/mL)/d, dT = .1/d, dI = 1/d, k = 250 virus/cell/d, c = 25/d. For these parameter values R 0 = 3. With treatment, where is the treatment efficacy. The initial condition for was T(0) = λ /dT, I(0) = 10−3 cell/uL/d, V(0) = 0.
