Figure 5.
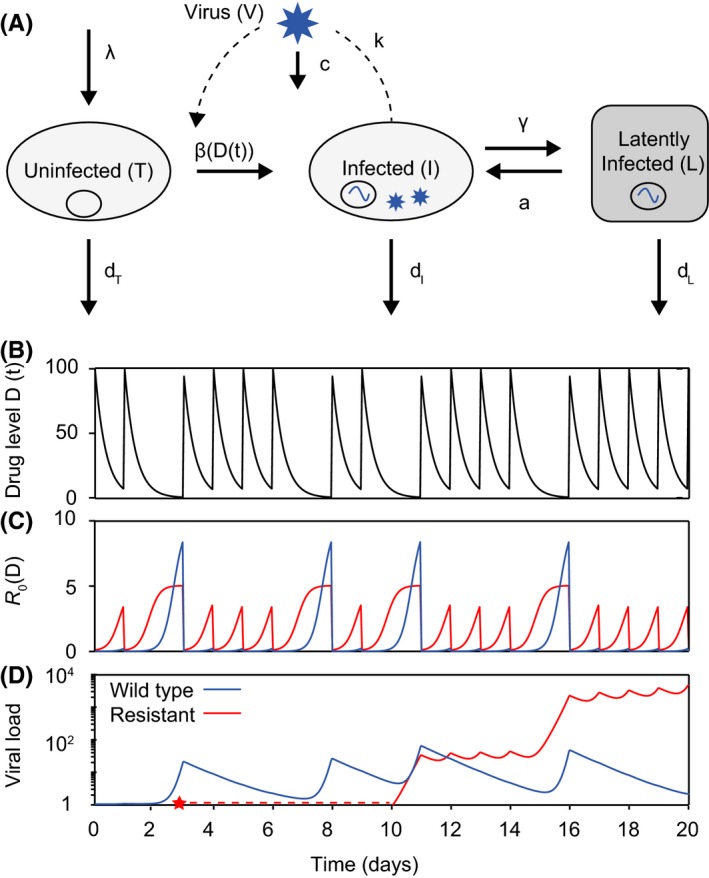
An augmented viral dynamics model can be used to simulate antiretroviral therapy and the evolution of drug resistance. (A) Basic viral dynamics model with the addition of a population of latently infected cells. A separate strain of virus, and the cells it infects, can be tracked for each genotype (V i , I i , L i). (B) Drug levels over time for a pill taken daily, and assumed to increase to maximum concentration immediately afterwards then decay exponentially. Each dose is taken with a 70% probability. (C) Basic reproductive number over time as a function of drug levels. (D) Levels of wildtype and resistant virus over time. At time zero, there is no resistant strain, but it is produced via mutation from the wildtype at the point indicated by the red star. Drug parameters: IC 50 = 1, C max = 100, m = 1, half‐life=6 hours. The resistant mutant has a 10‐fold increase in IC 50 and a twofold decrease in baseline fitness. Baseline R 0 = 10.
