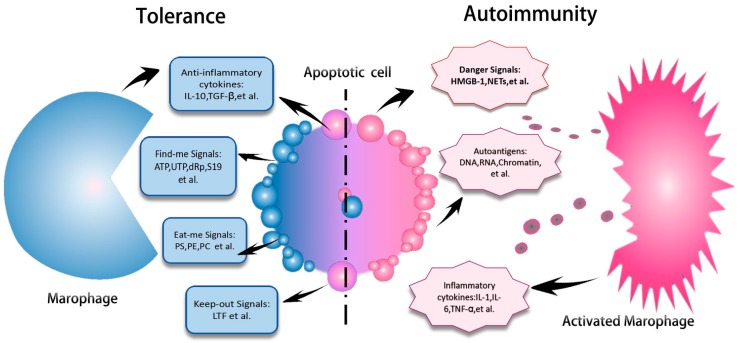
Figure 2.
Apoptotic cells induce immune tolerance and autoimmunity. Early apoptotic cells secrete anti-inflammatory cytokines—such as IL-10, TGF-beta—and express find-me (ATP, UTP, dRp S19), eat-me (PS, PE, PC), and keep-out (LTF) signals to macrophage for tolerance induction. However, when the clearance of early apoptotic cells is impaired, they will undergo late apoptotic process and release danger signals such as HMGB-1 and NETs as well as exposure auto-antigens (DNA, RNA, and chromatin). Macrophages are activated by these danger signals and then produce inflammatory cytokines—including IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-α—which may contribute to the development of autoimmune disorders. ATP, adenosine triphosphate; UTP, uridine triphosphate; dRp S19, dimer of ribosomal protein S19; PS, phosphatidylserine, PC, phosphatidylcholine; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; LTF, Lactotransferrin.