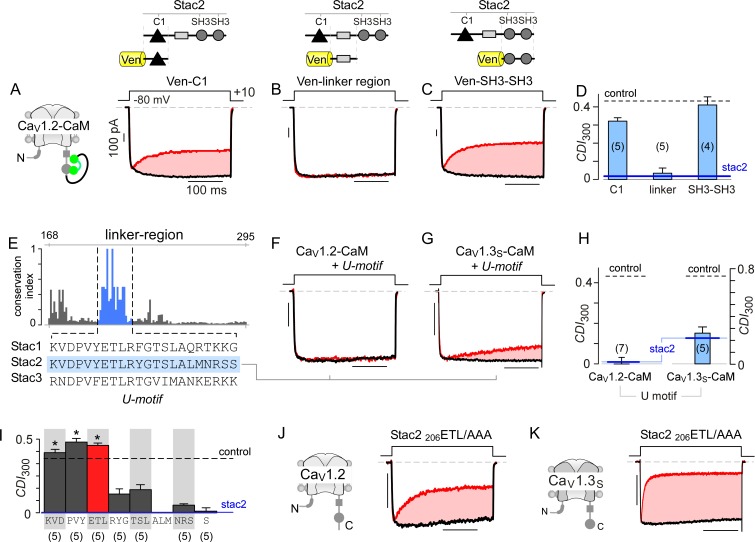
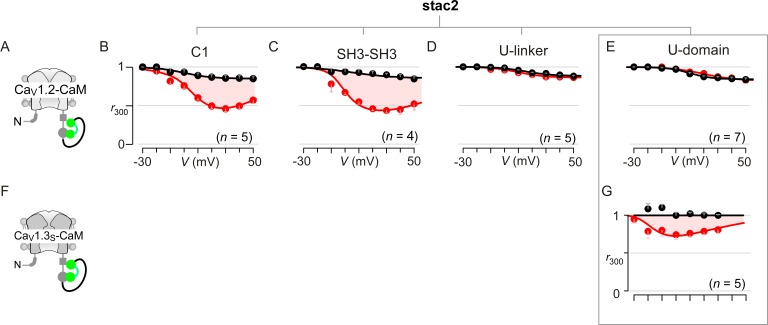
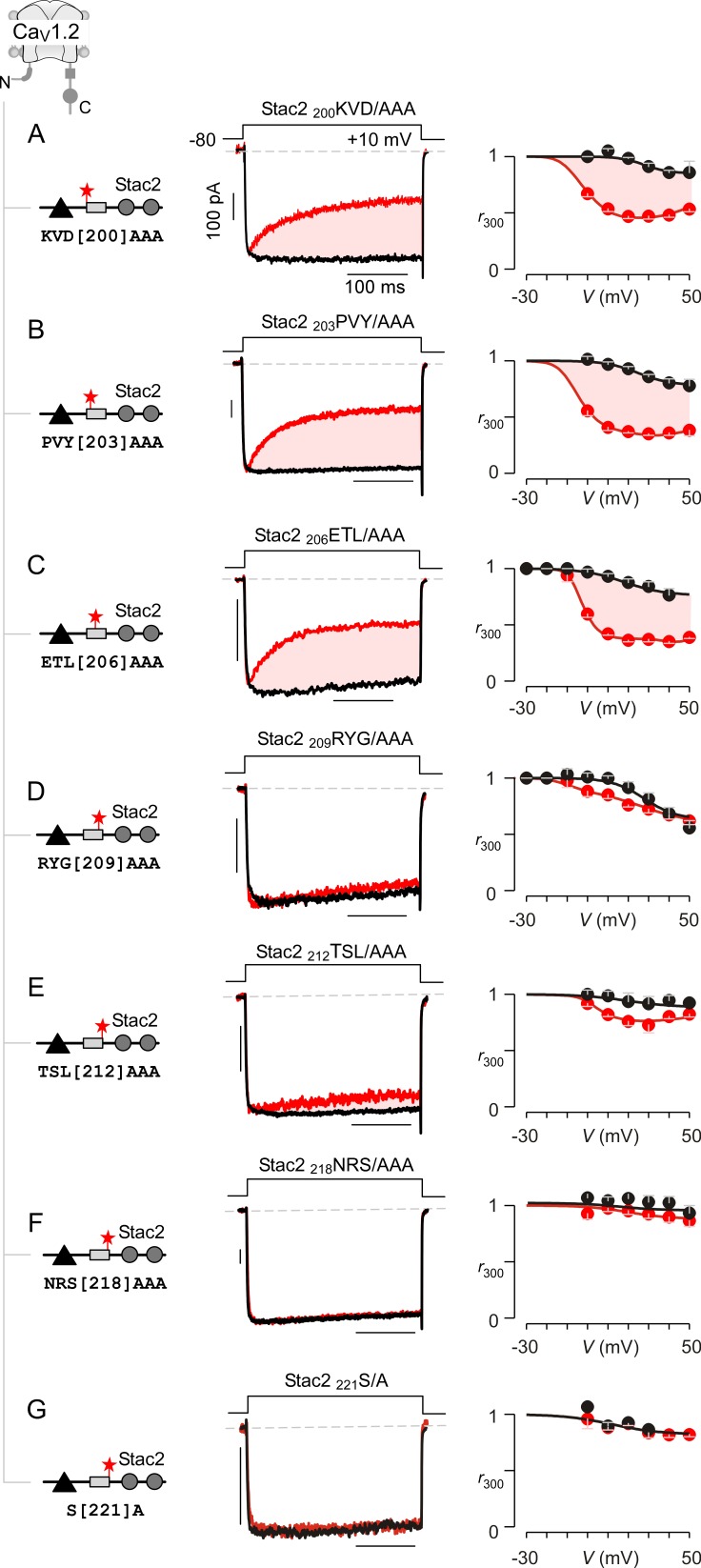
Figure 5. Stac U-domain is a minimal effect domain for suppression of CaV1 CDI.
(A–C) To localize an effector motif for stac2, CDI of CaV1.2-CaM was quantified in the presence of three stac subdomains: (1) C1, (2) linker region, and (3) SH3-SH3. Exemplar traces in response to a +10 mV voltage-step depolarization show robust CDI of CaV1.2-CaM in the presence of C1 (A), and SH3-SH3 (C) domains. Co-expression of the linker-region is sufficient to suppress CDI of CaV1.2-CaM (B). Format as in Figure 1A. (D) Bar graph summarizes population data for CaV1.2-CaM CDI in the presence of the three stac subdomains. Each bar, mean ±S.E.M of CDI300 at +10 mV from specified number of cells. CDI levels in the presence (solid blue line) and absence (dashed gray line) of full-length stac2 is reproduced for comparison. (E) Bar graph shows degree of conservation for the linker region across 770 orthologs of stac2. A well conserved subsegment termed U-domain is shaded blue. (F–G) Co-expression of U-domain is sufficient to abolish CDI of CaV1.2-CaM (F) and CaV1.3-CaM (G). Format as in Figure 1A. (H) Bar graph displays population data for CDI of CaV1.2-CaM and CaV1.3-CaM in the presence of U-domain. Each bar, mean ±S.E.M of CDI300 at +10 mV from specified number of cells. Dashed line, baseline CDI for both channels in the absence of stac2. Blue line, CDI of both channels in the presence of full-length stac2. (I) Systematic alanine scanning mutagenesis of the U-domain reveals critical determinants for stac-mediated suppression of CaV1.2 CDI. For comparison, CaV1.2 CDI in the presence (blue line) and absence (black dashed line) of stac2 are shown. Stac2 mutants 200KVD/AAA, 203PVY/AAA, 206ETL/AAA fully abolish stac2-mediated CDI suppression. (J) Exemplar currents show that stac2 mutant 206ETL/AAA eliminates stac’s ability to suppress CaV1.2 CDI. Format as in Figure 1A. (K) Stac2 206ETL/AAA also fails to inhibit CDI of CaV1.3S. Format as in Figure 1A.