FIGURE 1.
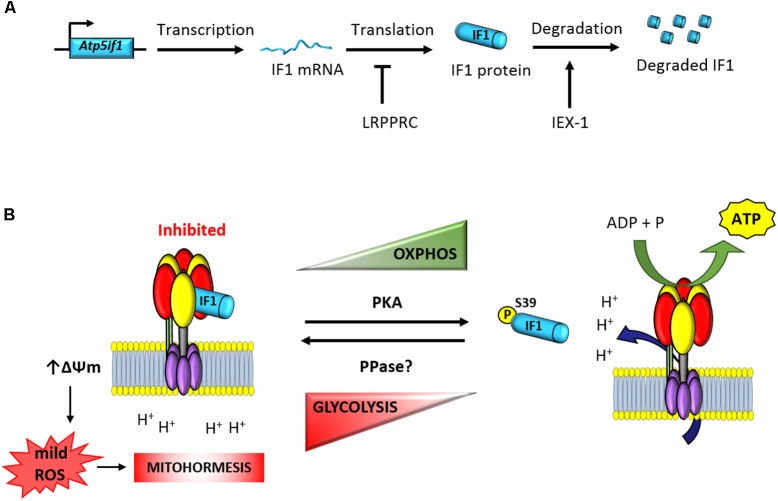
Posttranscriptional regulation of the expression and activity of IF1. (A) The expression of the short-lived IF1 protein is tissue-specific and regulated at posttranscriptional levels (Sanchez-Arago et al., 2013b,c). The mRNA binding protein LRPPRC participates in the negative control of IF1 expression (Mourier et al., 2014). Moreover, IEX-1 interacts with IF1 to target the protein to degradation (Shen et al., 2009). (B) The phosphorylation of IF1 by PKA-mediated prevents its binding to the ATP synthase and allows efficient synthesis of ATP (Garcia-Bermudez et al., 2015). In contrast, dephosphorylated IF1 binds the ATP synthase and inhibits ATP synthesis (Garcia-Bermudez et al., 2015). Inhibition of the enzyme triggers the raise in mitochondrial membrane potential and the production of mitochondrial ROS (Sanchez-Cenizo et al., 2010). mtROS act as second messengers to signal in the nucleus mitohormetic responses. Atp5if1, mouse gene of ATP synthase inhibitory factor 1; LRPPRC, leucine-rich pentatricopeptide repeat motif-containing protein; IEX-1, immediate early response X-1; PKA, protein kinase A; PPase, protein phosphatase; ΔΨm, mitochondrial membrane potential.