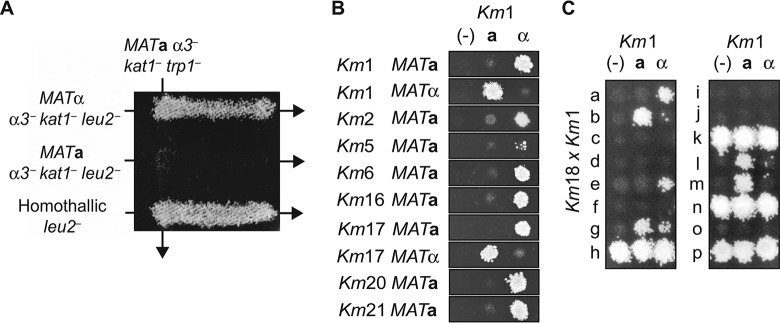
FIG 2.
Creation of heterothallic K. marxianus strains. (A) Auxotrophic mating assay of Km1 strains. Shown are results from strains Km1 MATα α3– kat1– leu2–, Km1 MATa α3– kat1– leu2–, and homothallic Km1 leu2–, streaked through strain Km1 MATa α3– kat1– trp1– on 2% glucose plates and replica plated onto SCD − (Leu, Trp) plates after 2 days. Diploid growth is seen only upon sexual crossing between strains with opposite mating types or with homothallic haploid strains. (B) Auxotrophic mating assay of several α3– kat1– leu2– triple-inactivation strains and Km1 MATa α3– kat1– trp1– or Km1 MATα α3– kat1– trp1–. Putative heterothallic strains were spotted over the negative control (−), the Km1 MATa α3– kat1– trp1– reference (a), or the Km1 MATα α3– kat1– trp1– reference (α) on glucose plates for mating. Replica plating onto SCD − (Leu, Trp) results in diploid growth. (C) The wild homothallic isolate Km18 was made trp– by UV mutagenesis and crossed with heterothallic Km1 MATa α3– kat1– leu2–. Diploids were sporulated, 16 spores were isolated (a through p) and germinated, and the resulting haploids were screened for heterothallic strains by crossing with Km1 MATa α3– kat1– trp1– or Km1 MATα α3– kat1– trp1–. Screened haploids were auxotrophic strains unable to mate (c, d, f, i, j, and o), possible trp– revertants (h, k, n, and p), homothallic (g), or heterothallic (a, b, e, l, and m).