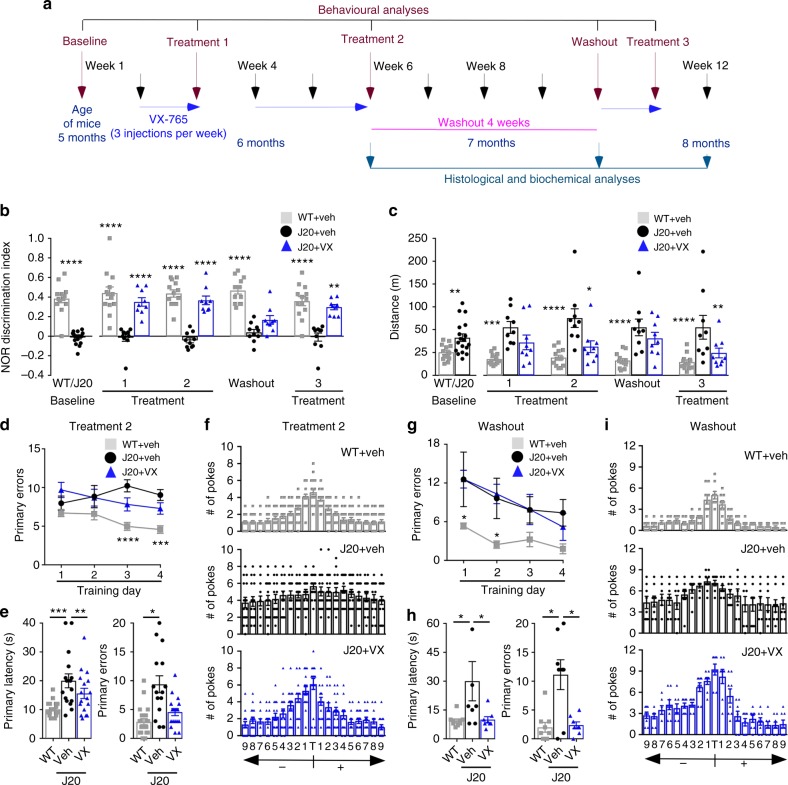
Fig. 1.
VX-765 treatment restores J20 mice cognitive function. a Experimental treatment paradigm. b NOR Discrimination index from vehicle-treated WT (grey squares), vehicle-treated J20 (black circles) and VX-765-treated J20 (blue triangles). Each mouse tested is represented by one symbol. Data represent mean and s.e.m. (Treatment, F(2,20) = 85.8, p < 0.0001; Time, F(4,80) = 4.188, p = 0.0039; Treatment × Time, F(8,80) = 3.599, p = 0013). c Distance travelled during open field task (Treatment, F(2,19) = 11.47, p = 0.0005; Treatment × Time, F(8,76) = 5.69, p < 0.0001). b, c Two-way repeated-measures ANOVA and Dunnett’s post-hoc versus J20 + vehicle, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. d–i Barnes maze: learning acquisition # of primary errors during d T2 (Treatment, F(2,212) = 19.93, p < 0.0001) and g WO (Treatment, F(2,56) = 10.86, p = 0.001; Training day, F(3,56) = 3.392, p < 0.0241). d, g Two-way repeated-measures ANOVA and Dunnett’s post-hoc versus J20 + vehicle *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. Probe primary latency and errors during e T2 and h WO. Target preference: # of pokes of each hole labelled +1 to +9 to the right or −1 to −9 to the left of the target (T) during the probe after f T2 and i WO (T2 primary latency, F(2,52) = 5.879, p = 0.0050; T2 primary errors, F(2,52) = 9.998, p = 0.0002; WO primary latency, F(2,22) = 4.076, p = 0.0312; WO primary errors, F(2,22) = 10.84, p = 0.0005). e, h ANOVA, Tukey’s post-hoc, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001