Figure 4.
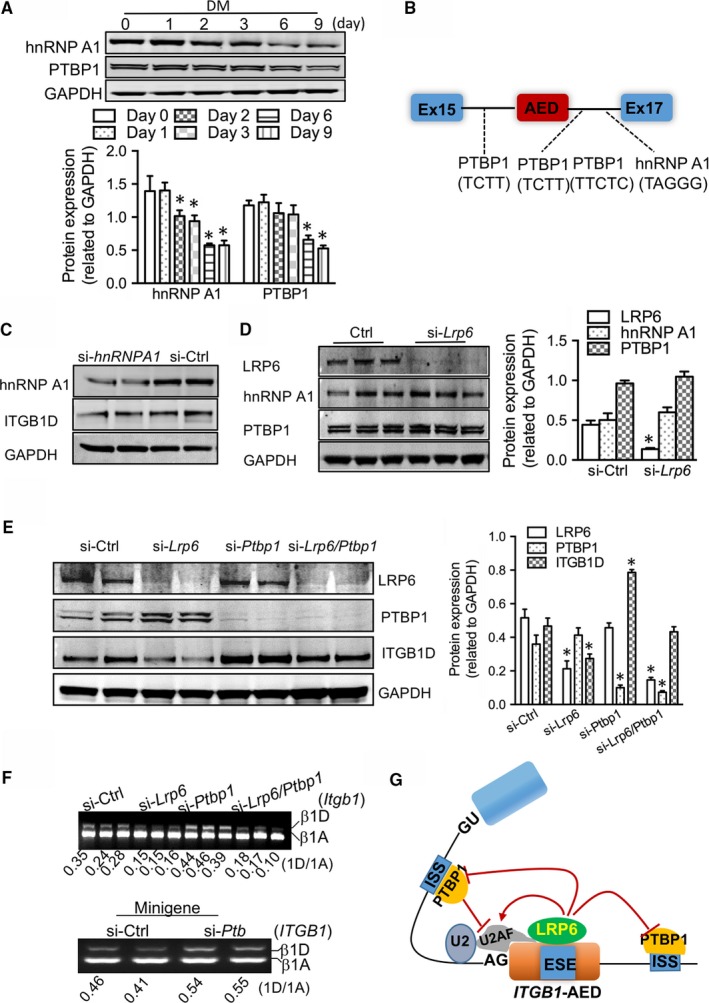
Roles of splicing repressors in the splicing switching of Itgb1 isoforms. (A) Western blotting examination of hnRNP A1 and PTB proteins during myodifferentiation of C2C12 myoblasts. DM, differentiation medium. Bottom: pooled data. *P < .05 compared with day 0. (B) Schematic of hnRNP A1 and PTB‐binding sites in the flanking introns of alternative exon D in the splicing reporter of Itgb1. (C) Effects of hnRNP A1 on the protein expression of ITGB1D in myocytes. (D) Effects of LRP6 on the protein expression of hnRNP A1 and PTBP1. The proteins were extracted from neonatal cardiomyocytes subject to hnRNP A1‐ or Lrp6‐siRNAs for 48 h. Right: pooled data. *P < .05 compared with si‐Ctrl. (E‐F) Effects of the splice repressor PTBP1 on the splicing of Itgb1D in the presence and absence of LRP6 in culture neonatal cardiomyocytes. Western blotting examination of LRP6, PTBP1 and ITGB1D proteins (E). E‐right: pooled data. *P < .05 compared with si‐Ctrl. (F‐top) Gel electrophoresis analysis of Itgb1 RNAs; (F‐bottom) gel electrophoresis analysis of the specific activity of PTBP1 on Itgb1 pre‐mRNA using the minigene. (G) Model of the LRP6‐mediated splicing of Itgb1D in striated muscle cells. Representative blots from five independent experiments with similar results are shown
