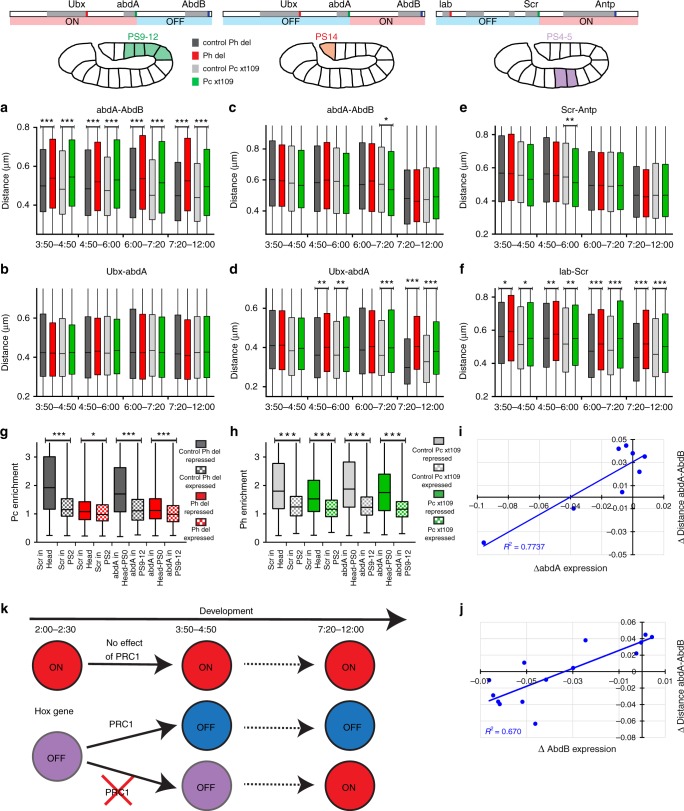
Fig. 5.
cPRC1 only compacts chromatin in the repressed regions of the BX-C and ANT-C domains. a–f Box plots displaying distributions of the distances abdA–AbdB (a, c), Ubx–abdA (b, d), Scr–Antp (e), and lab–Scr (f) measured in the cell nuclei of Phdel embryos (red) and their respective controls (dark gray) or PcXT109 embryos (green) and their respective controls (light gray). Measurements were made in PS9–12 (a, b), PS14 (c, d), and PS4–5 (e, f) during development. Distances distribution are comprised between 0 and 1.5 µm. g, h Box plots presenting Pc (g) and Ph (h) enrichments at Scr and abdA FISH spots. Distribution of Pc and Ph enrichments are comprised between 0.2 and 11.33. The lower and upper bounds of the colored rectangles correspond to the first and third quartiles, whereas the middle bars indicate the median distances (a–h). Significant differences are indicated (Mann–Whitney, U-test, two-tailed, *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001) (a–h). i, j Scatterplots showing correlations between the differential effect of Ph and Pc on the distance abdA–AbdB at 3:50–4:50 and the differential effect of Ph and Pc on abdA or AbdB expression at 4:50–6:00. Each point corresponds to one PS where abdA (i) or AbdB (j) are repressed in WT embryos. k Schematic diagram summarizing the effects of PRC1 on Hox gene folding and transcription. Circles represent silenced (OFF) or transcribed (ON) chromatin associated with Hox genes (red, open; purple, partly compact; blue fully compact). cPRC1 has no effect when Hox genes are expressed and chromatin is open. When Hox genes are repressed, cPRC1 compacts their chromatin during early embryogenesis and they will remain silenced. Without cPRC1, this compaction cannot occur and silenced Hox genes might become subsequently transcribed