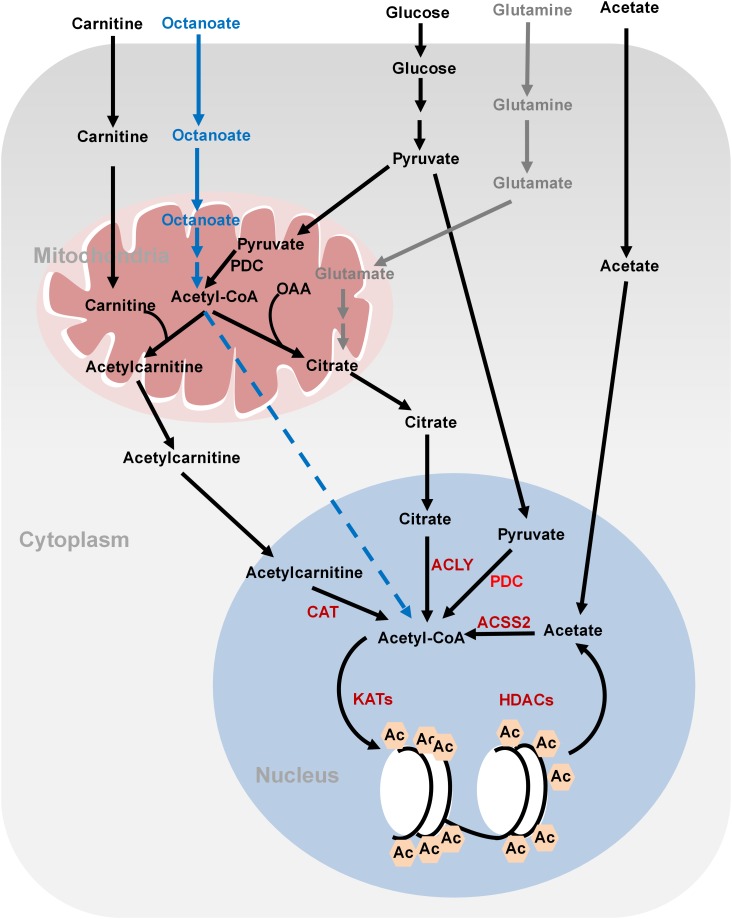
FIGURE 1.
Metabolism of acetyl-CoA and histone acetylation. Glucose-derived pyruvate is metabolized to acetyl-CoA by PDC in the mitochondria. Mitochondrial acetyl-CoA needs to be converted to citrate or acetylcarnitine in order to be exported into cytoplasm and nucleus. In the nucleus, acetyl-CoA is regenerated from citrate and acetylcarnitine by ATP-citrate lyase (ACLY) and carnitine acetyltransferase (CAT), respectively, for histone acetylation. Nucleus acetyl-CoA can also be produced from glucose-derived pyruvate by nucleus PDC. Fatty acids (octanoate) can be oxidized to produce acetyl-CoA in the mitochondria but it is unknown how it is transported into the nucleus. ACSS2 synthesizes acetyl-CoA from acetate, which is derived from the media or deacetylation reactions. Glutamine can be used to synthesize citrate through reductive carboxylation in the mitochondria. Citrate can then be translocated into the nucleus to generate nucleus acetyl-CoA. OAA, oxaloacetate; ACLY, ATP-citrate lyase; PDC, pyruvate dehydrogenase complex; ACSS2, acetyl-CoA synthetase short chain family member 2; CAT, carnitine acetyltransferase; Ac, acetylation.