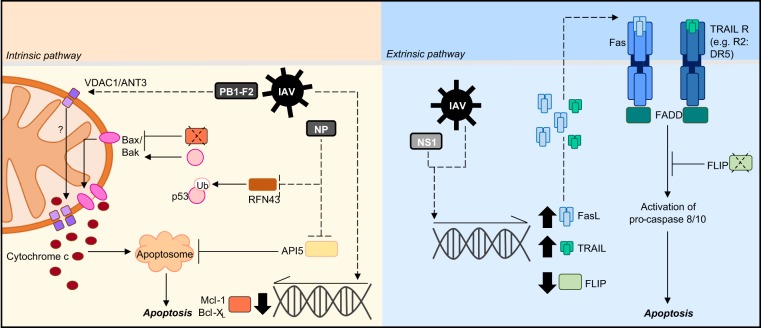
Fig. 2. Molecular mechanisms of IAV-induced apoptosis.
IAV can induce host cell apoptosis through either the intrinsic or extrinsic pathway. To induce apoptosis via the intrinsic pathway, IAV infection can promote the downregulation of anti-apoptotic proteins (Mcl-1/Bcl-XL) and p53 stabilisation. In turn, these mechanisms activate bax/bak to facilitate mitochondrial membrane pore formation and allow cytochrome c release. The IAV protein PB1-F2 can interact with VDAC1 and ANT3 to promote mitochondria outer and inner membrane permeabilisation and the release of pro-apoptotic molecules. Additionally, IAV infection can inhibit the anti-apoptotic protein API5 which usually functions to restrict apoptosome formation. IAV infection can also induce apoptosis through the extrinsic pathway by increasing the expression of death receptor ligands including FasL and TRAIL. Furthermore, infection can downregulate the expression of the anti-apoptotic protein FLIP which usually functions to limit Fas-mediated apoptosis. Dotted lines refer to IAV-targeted processes, solid lines refer to host cell processes