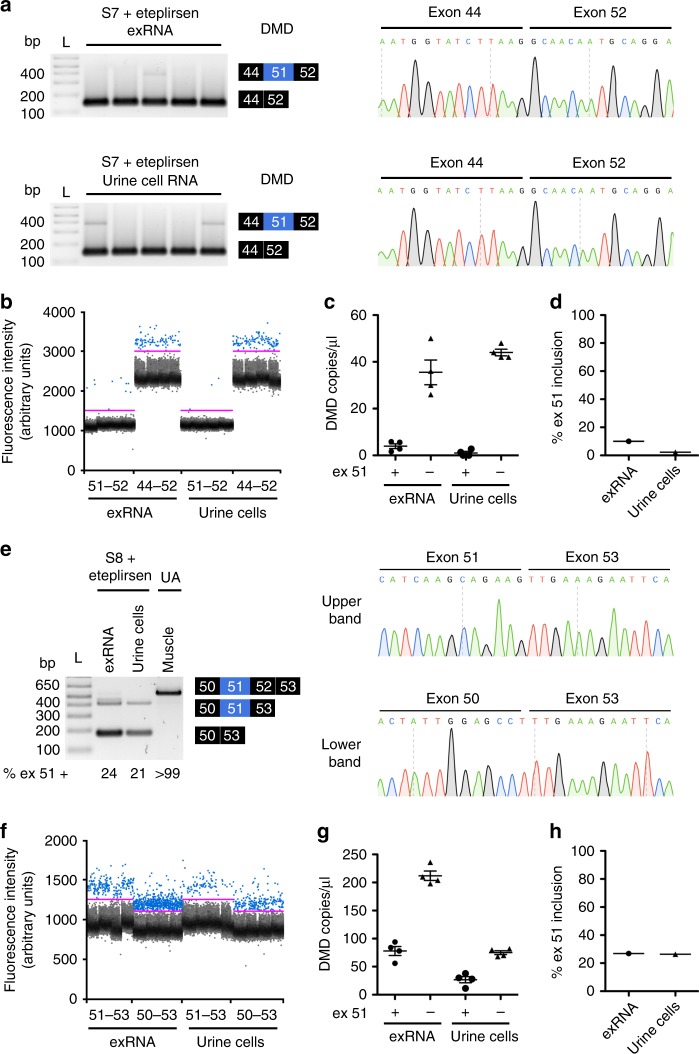
Fig. 10.
Pharmacologic exon skipping activity of eteplirsen in human urine. Using RT-PCR and ddPCR, we examined urine exRNA and urine cell RNA in two non-ambulatory individuals with DMD who have been treated with 30 mg/kg eteplirsen weekly for ~3 years. a Left, using RT-PCR and primers targeting exons 44 and 52, two bands are identified in urine exRNA and urine cell total RNA (N = 5 replicates each) from a non-ambulatory 17 year-old DMD patient (S7) with an exon 45–50 deletion. Right, sequencing of the lower-band PCR product. b ddPCR analysis of urine exRNA and urine cell total RNA (N = 4 replicates each) from S7 using separate probe sets that are specific for DMD transcripts with exon 51 included (51–52) or skipped (44–52)35. c Individual data points indicate quantification of DMD splice products in urine exRNA and urine cell total RNA (N = 4 replicates each) that have exon 51 included (+) or skipped (−) as copies per microliter of cDNA. d Calculation of percent exon 51 inclusion in urine exRNA and urine cells using the data in c. e Left, using RT-PCR and primers targeting exons 49 and 53, two bands are identified in urine exRNA and urine cell total RNA from a non-ambulatory 19 year-old DMD patient (S8) with an exon 52 deletion. UA muscle tissue RNA served as a control. Right, sequencing of the urine exRNA PCR products. f ddPCR analysis of urine exRNA and urine cell total RNA (N = 4 replicates each) from S8 using separate probe sets that are specific for DMD 52 deletion transcripts with exon 51 included (51–53) or skipped (50–53)35. g Individual data points indicate quantification of DMD splice products in urine exRNA and urine cell total RNA (N = 4 replicates each) that have exon 51 included (+) or skipped (−) as copies per microliter of cDNA. h Calculation of percent exon 51 inclusion in urine exRNA and urine cells using the data in (g). All error bars indicate mean ± s.e.m.