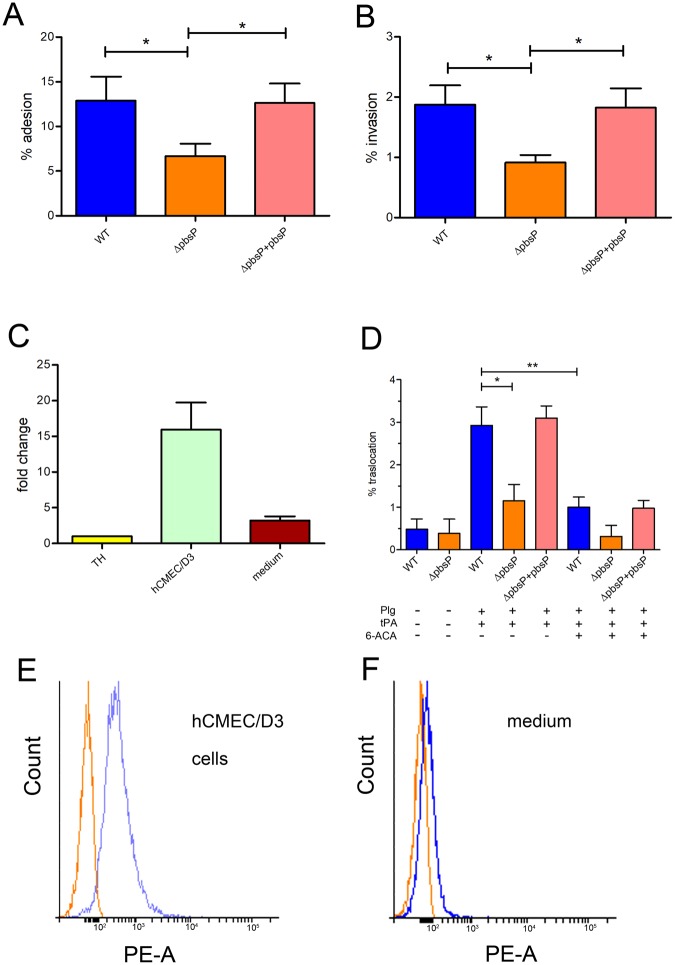
Figure 6.
PbsP is required for adhesion to and transmigration across brain endothelial cells by CC17 GBS. (A,B and D) GBS strains were compared for their ability to interact with endothelial cells. WT, BM110 wild-type strain; ΔpbsP, isogenic BM110 pbsP deletion mutant; ΔpbsP + pbsP, ΔpbsP strain carrying a complementing vector with constitutive pbsP expression. Results are means ± SD from four independent experiments performed in triplicate. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 by Bonferroni test and one way ANOVA. Adhesion (A) invasion (B) and traslocation (D) were assessed using the brain endothelial cell line hCMEC/D3. Plg, plasminogen; (tPA), tissue Plg activator; (6-ACA), 6-amino-n-caproic acid (100 nM). (C) RT-PCR analysis of pbsP mRNA levels in BM110 GBS incubated for 3 h in the presence of hCMEC/D3 cells (hCMEC/D3) or fresh, cell-free hCMEC/D3 culture medium (cell culture medium). Values were normalized for those observed in bacteria grown in Todd-Hewitt broth (TH). (E, F) Immunofluorescence flow cytometry analysis using mouse polyclonal anti-PbsP serum (blue line) or control anti-GST serum (red line) of PbsP surface expression in BM110 GBS exposed to cultured brain micro-vascular endothelial cells as detailed in (C).