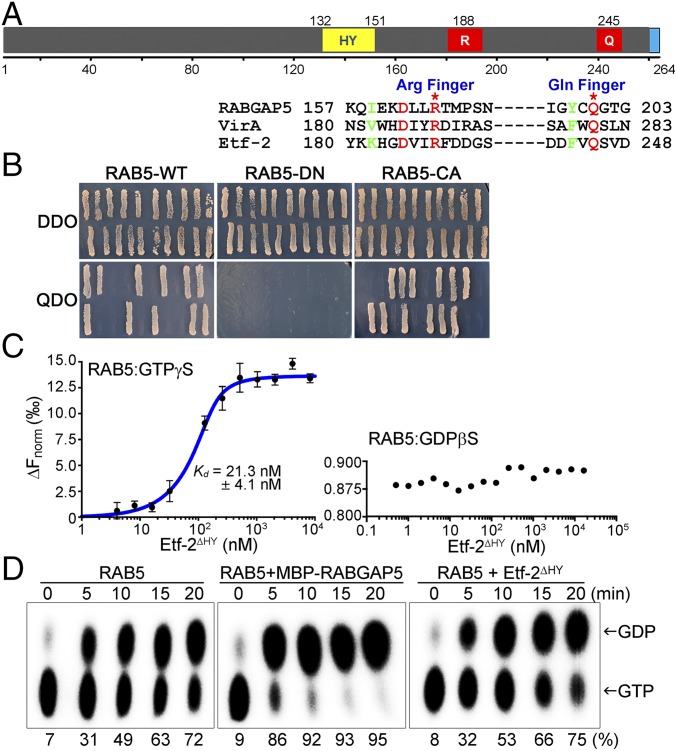
Fig. 4.
Etf-2 has a GAP TBC-like dual catalytic finger motif that directly binds to RAB5-GTP but lacks RAB5 GAP activity. (A, Upper) Putative domain structures of Etf-2. Numbers indicate amino acid positions. Q, glutamine finger; R, arginine finger; the blue boxed domain is the putative T4SS signal. (Lower) Amino acid sequence alignment of Etf-2 with TBC domains of RABGAP5 and Shigella VirA that have RAB1 GAP activity. Etf-2 has the GAP TBC-like dual (Arg and Glu) catalytic finger motif (red) near its C terminus. (B) Direct interaction of full-length Etf-2 with RAB5-WT, -DN, and -CA was tested using the yeast two-hybrid assay. Twenty independent colonies were tested on SD/−Leu/−Trp double-dropout (DDO) and SD/−Leu/−Trp/−His/−Ade quadruple-dropout (QDO) agar plates. Growth on QDO plates indicated a specific interaction between Etf-2 and RAB5-WT or -CA. (C) MST assay with purified proteins demonstrating binding of RAB5A to Etf-2∆HY in a GTP-dependent manner. RAB5A was fluorescently labeled with Tris-nitrilotriacetic acid at fixed concentrations ranging from 5 to 200 nM and was preincubated with GTPγS or GDPβS; binding was assessed with unlabeled Etf-2∆HY from the low picomolar range to 100 µM. RAB5A binding to Etf-2∆HY was observed only in RAB5A-GTPγS samples. The determined Kd value is shown. Data are shown as mean ± SD (n = 4). (D) GAP activity of Etf-2∆HY. GST-RAB5 that had been affinity-purified on GST resin was preloaded with [α-32P]GTP followed by a GTP hydrolysis reaction in the absence or presence of RABGAP5 or Etf-2∆HY. Samples were taken at the indicated times and subjected to TLC followed by autoradiography and PhosphorImager analysis to visualize and quantify the radiolabeled hydrolysis product (32P-GDP) from substrate (32P-GTP) as indicated. The percentage values indicate the amount of GDP produced from GTP.