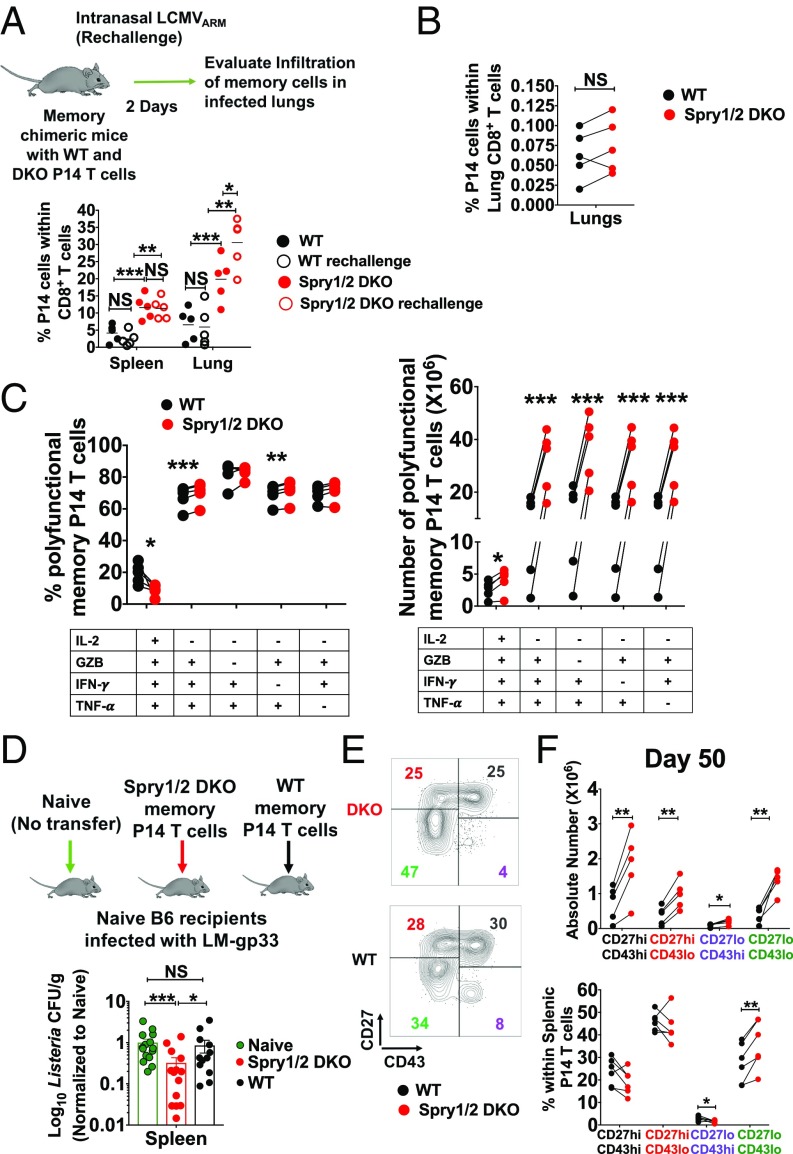
Fig. 4.
The absence of Spry1/2 promotes the formation of larger numbers of polyfunctional memory CD8+ T cells with superior protective capacity. (A) Chimeric animals generated by transferring WT and DKO P14 T cells were immunized i.p. with 2 × 105 pfu LCMVARM and 50 d later were rechallenged i.n. with 8 × 105 pfu of LCMVARM. Recall responses of WT and DKO P14 T cells were measured 2 d later in the spleen and lung. (B) Memory P14 T cells from WT and DKO chimeric animals were purified by flow cytometry, mixed at a 1:1 ratio, and adoptively transferred into naive mice. Chimeric mice were then challenged i.n. with 8 × 105 pfu of LCMVARM, and the proportion of P14 T cells infiltrating the lungs was measured. (C) The frequency (Left) and number (Right) of polyfunctional memory P14 T cells after ex vivo stimulation with gp33 peptide. (D) WT and Spry1/2 DKO memory P14 T cells were purified from the spleen and pLNs of donor chimeric animals by flow cytometry and were retransferred into naive hosts that were then challenged with recombinant L. monocytogenes expressing LCMV gp33 (LM-gp33). (E and F) The absolute number (E) and fraction of each memory T cell subset (F) was measured based on differential surface expression of CD27 and CD43 on memory P14 T cells in the spleen at day 50 after LCMVARM infection. Data are representative of two independent experiments. Each point represents one individual mouse. The P values represent the difference between WT and DKO P14 T cells (paired t test): *P < 0.05, **P < 0.009, and ***P < 0.0005. NS, not significant.