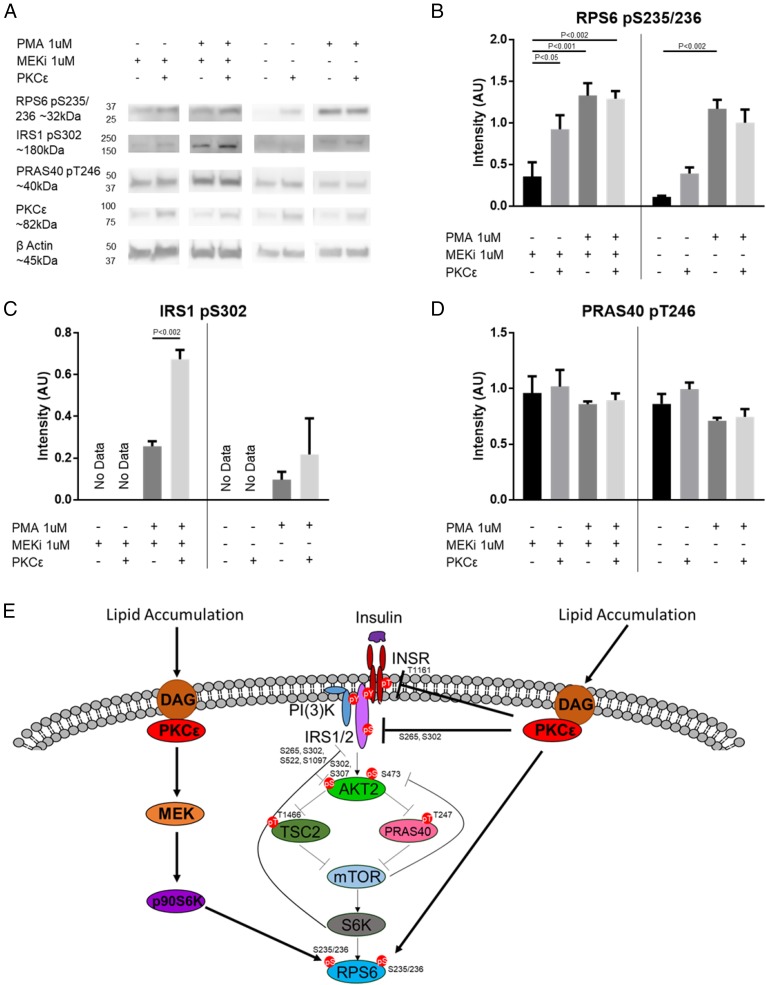
Fig. 4.
PKCε can cross talk with p70S6K substrates. (A) Western blot of p70S6K1/p70S6K2 DKO cells with or without WT PKCε transfection, treated with or without 1 μM MEKi, followed by treatment with or without 1 μM PMA. Densitometry for RPS6 S235/236 phosphorylation (different exposures for −MEKi and +MEKi) (B), IRS1 S302 phosphorylation (C), or PRAS40 T246 phosphorylation (D). n = 3. Bands are normalized to β-actin. Vertical bars separate +MEKi and −MEKi. P values for two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparisons test are as indicated. Full Western blots with selected lanes indicated in SI Appendix, Fig. S6B. (E) Model of PKCε modulation of canonical insulin signaling. In addition to modulating the INSR itself and other known members of the insulin signaling pathway, PKCε may influence insulin signaling through phosphoproteins modulated by the PKCε ASO alone (categories II and VIII) or by the PKCε ASO and HFD (categories III and VII) that were shown by siRNA screen to activate (blue) or inhibit (yellow) AKT S473 phosphorylation; direct targets of PKCε are shown by the solid lines.