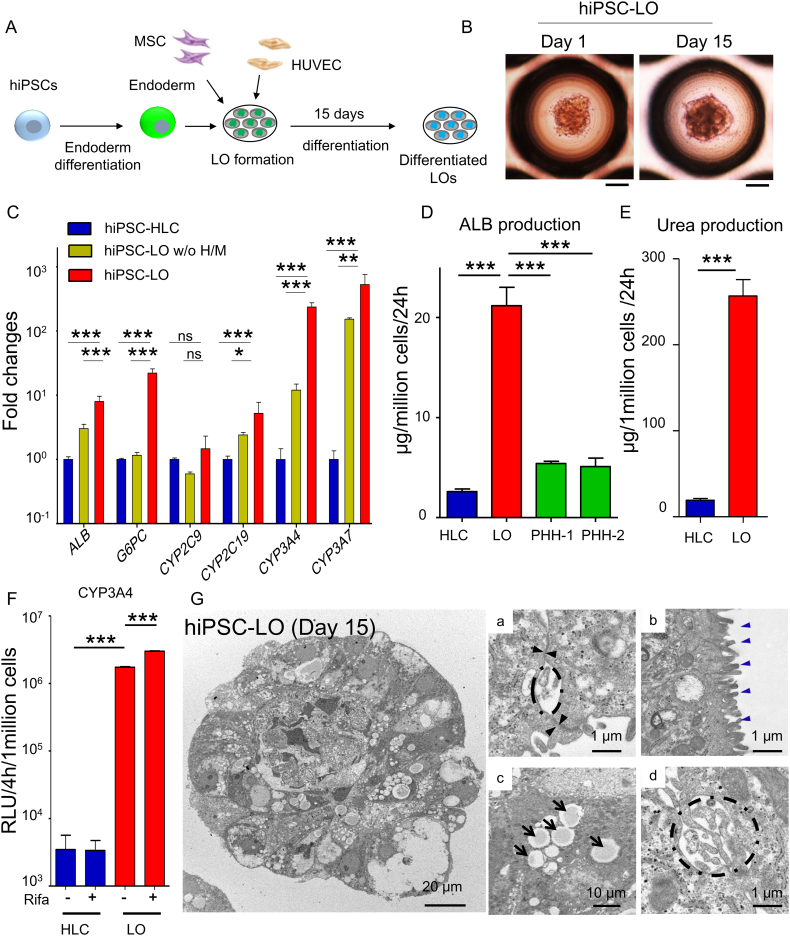
Fig. 1.
Generation of functional liver organoids from hiPSCs.
(A) Schematic representation of generation and differentiation of liver organoids (LOs) from hiPSCs. After 15 days of differentiation, differentiated LOs were collected and analyzed. (B) Morphology of hiPSC-LOs at day 1 and day 15. Scale bar, 100 μm. (C) Q-PCR analysis showing expression of hepatic genes: ALB, G6PC, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP3A4, and CYP3A7 in hiPSC-HLCs (n = 4), differentiated hiPSC-LOs w/o H/M (deletion of HUVEC and MSC at LOs generation) (n = 4), and differentiated hiPSC-LOs (n = 4). (D) ELISA for ALB secretion of hiPSC-HLCs (n = 9), differentiated hiPSC-LOs (n = 11), PHH-1(24 h cultured, n = 3), and PHH-2 (24 h cultured, n = 3). (E) Quantification of urea production in hiPSC-HLCs (n = 8) and differentiated hiPSC-LOs (Day 15, n = 8). (F) Quantification of CYP3A activity in differentiated hiPSC-HLCs (n = 4) and hiPSC-LOs (n = 4), with or without 25 μM rifampicin treatment. (G) Transmission electron microscopy analysis showing ultrastructure of differentiated hiPSC-LO. (a) Tight junction (black arrowhead), (b) Microvilli (blue arrowhead), (c) Lipid droplets (black arrow), and (d) Bile canaliculi (dotted line). *p < .05, **p < .01, ***p < .001; ns, not significant.