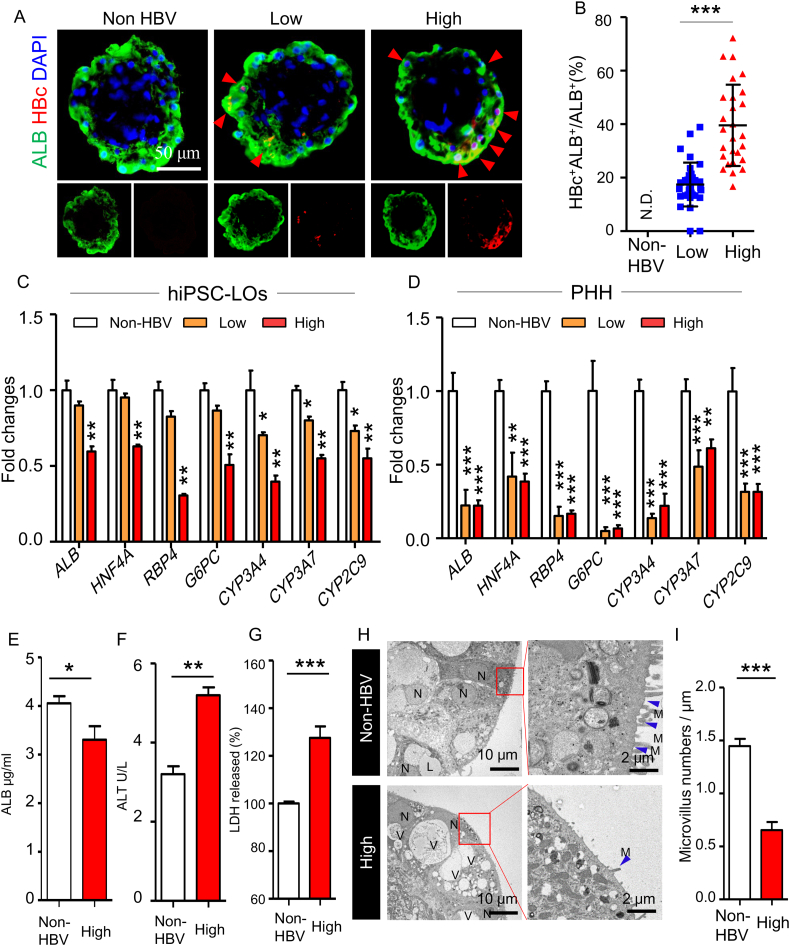
Fig. 4.
Induction of hepatic dysfunction in hiPSC liver organoids with HBV infection.
(A) Immunofluorescence analysis of HBc and ALB in hiPSC-LOs at doses of 0 (Non-HBV), 500 (low dose), and 5000 (high dose) GEq/cell infection at 10 dpi. (B) The percentage of ALB+HBc+ cells relative to that of total ALB+ cells, n = 22 liver organoids. (C) Q-PCR quantification of hepatic genes ALB, HNF4A, G6PC, RBP4, CYP3A4, CYP3A7, and CYP2C9 in non-, low-dose and high-dose HBV-infected hiPSC-LOs at 10 dpi, n = 4. (D) Q-PCR quantification of hepatic genes ALB, HNF4A, G6PC, RBP4, CYP3A4, CYP3A7, and CYP2C9 in non-, low-dose and high-dose HBV-infected PHH-2 at 10 dpi, n = 3. (E) ELISA analysis of ALB secretion in non- and high-dose HBV-infected hiPSC-LOs, n = 5. (F) Quantification of ALT in the supernatant of non- and high-dose HBV-infected hiPSC-LOs at 10 dpi, n = 5. (G) Detection of LDH in the supernatant of non- and high-dose HBV-infected hiPSC-LOs at 10 dpi, n = 5, non-HBV group used as a control. (H) Transmission electron microscopy analysis of the ultrastructure of hiPSC-LOs with non- and high-dose HBV infection at 10 dpi, N: nuclear; V: vacuole; L: lipid drop; blue arrow: microvilli. (I) Numbers of microvilli in non- and high-dose HBV infected hiPSC-LOs, n = 5.