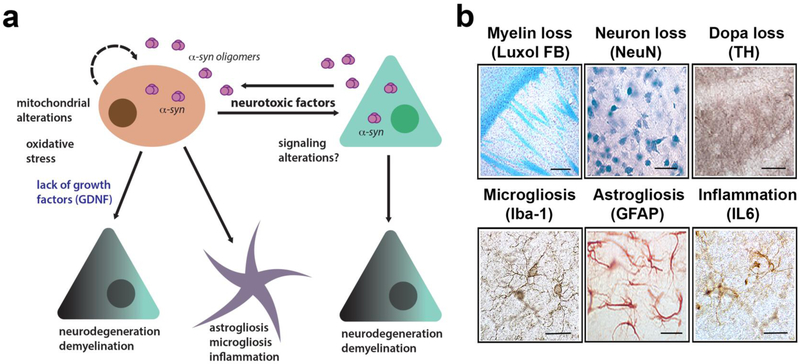
Figure 2.
Pathogenic mechanisms in MSA triggered by α-synuclein leading to neurodegeneration. (a) Diagrammatic representation of the hypothetical mechanisms neurodegeneration in MSA. α-Synuclein transmits from neurons to oligodendroglial cells leading to mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress and loss of trophic support of neurons (e.g.: GDNF), this, in turn, is associated with neuroinflammation, demyelination, and neuronal degeneration. (b) Characterization of neuropathology in the MBP-α-synuclein tg mice includes myelin loss (luxol fast blue, bar=100 μm), neuronal loss (NeuN, bar=50 μm), loss of DOPA fibers (tyr hydroxylase TH, bar=50 μm), microgliosis (Iba1, bar=25 μm), astrogliosis (GFAP, bar=25 μm) and IL6 expression (bar=25 μm). Images are from the striatum of the MBP Line1 age 12 months.