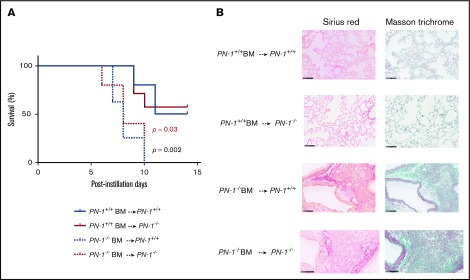
Figure 5.
Protective effect of PN-1 from BM cells in bleomycin-injured chimeric mice. PN-1−/− mice and their PN-1+/+ littermates were irradiated and underwent transplantation with BM from appropriated mice and allowed to recover for 5 weeks before bleomycin-induced lung injury. PN-1+/+ BM → PN-1+/+: PN-1+/+ mice receiving PN-1+/+ BM transplants (n = 10). PN-1−/− BM → PN-1+/+: PN-1+/+ mice receiving PN-1−/− BM transplants (n = 8). PN-1+/+ BM → PN-1−/−: PN-1−/− mice receiving PN-1+/+ BM transplants (n = 7). PN-1−/− BM → PN-1−/−: PN-1−/− mice receiving PN-1−/− BM transplants (n = 5). (A) Percentages of surviving mice undergoing transplantation were plotted over a 14-day period after bleomycin treatment. Log-rank test was used to compare the difference between similar recipient mice. P = .03 for PN-1+/+ BM → PN-1−/− vs PN-1−/− BM → PN-1−/−, and P = .002 for PN-1+/+ BM → PN-1+/+ vs PN-1−/− BM → PN-1+/+. (B) Masson’s trichrome and Sirius red stainings of lung withdrawn the day of euthanasia from PN-1+/+ and PN-1−/− chimeric mice. Representative images are shown. Scale bars, 100 µm.