Figure 6.
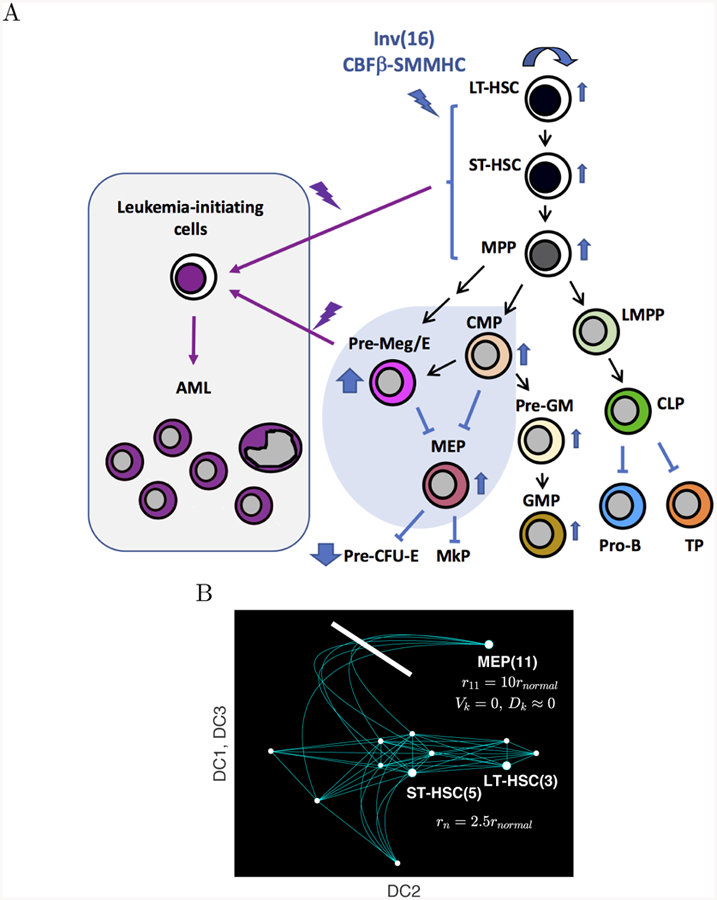
A) Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a cancer of aberrant differentiation and proliferation of hematopoietic progenitor cells. Previous studies demonstrated that expression of inv(16) leukemogenic fusion protein CBFβ-SMMHC results differentiation block at multiple hematopoetic stages along with expansion of preleukemic stem/progenitor cells and abnormal myeloid progenitors, including CMP, Pre-Meg/E and MEP. These preleukemic stem/progenitor cells and abnormal myeloid progenitors are susceptible to malignant transformation into leukemia-initiating cells that drive and sustain AML pathogenesis. B) Schematic illustration of AML pathogenesis in the differentiation continuum. To simulate inv(16) driven AML, the proliferation Rk(x) connecting the nodes 3, 5, and 11 is increased and the flow toward the node 11, Vk(x) and Dk(x) for k = I(i, 11) is blocked.
