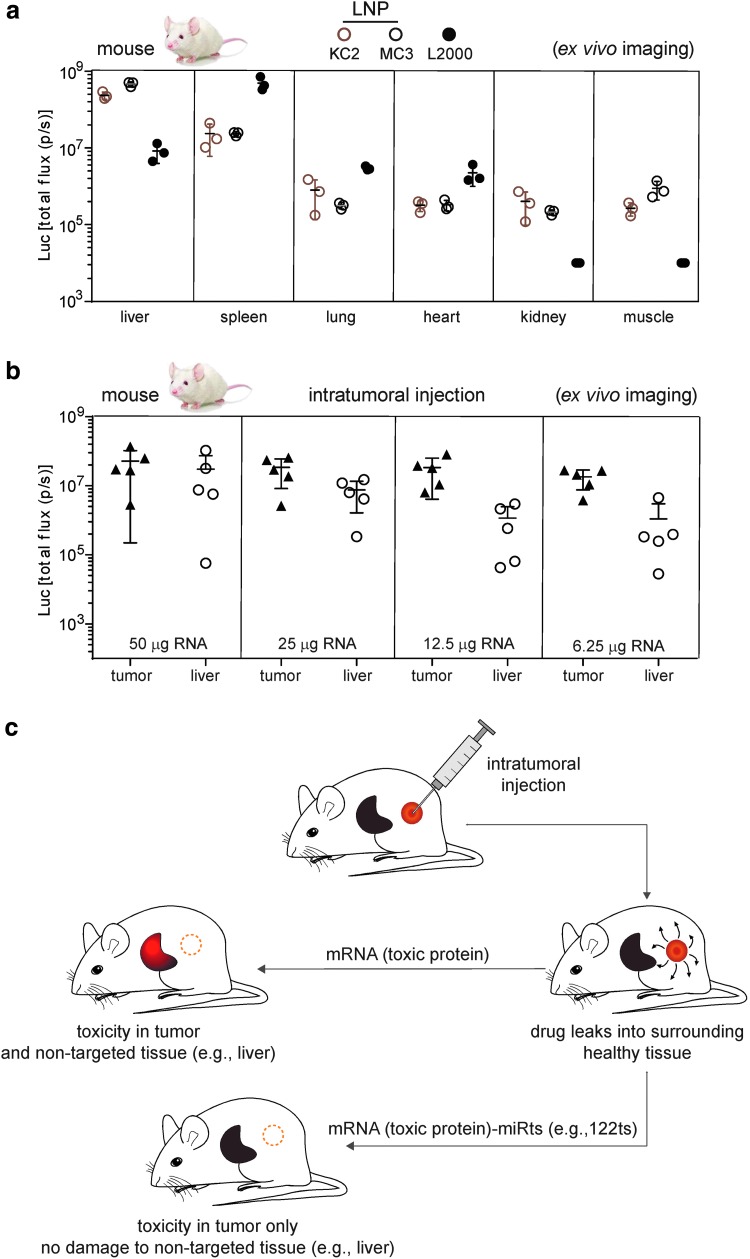
FIG. 1.
Nonspecific biodistribution of protein expression after mRNA delivery. (a) Intravenous delivery of mRNA results in protein expression in multiple tissues. Total flux (photons/s) from indicated organs 6 h after 1-methyl-pseudouridine (m1Ψ) Luc mRNA encapsulated in KC2 or MC3 LNPs or in complex with L2000 is intravenously administered to mice. (b) Intratumoral delivery of mRNA can lead to protein expression in liver. Total flux (photons/s) from tumor and liver 6 h after m1Ψ Luc mRNA encapsulated in MC3 LNP is administered to mice with subcutaneous MC38 tumor. (c) Schematic representation to illustrate the possible benefits of using a miRts in mRNAs to dampen off-target expression in mice. Intratumoral injection of an mRNA encoding a toxic protein can trigger cytotoxicity to kill tumor cells but may also damage a nontargeted tissue such as liver. miRts incorporation in the mRNA may restrict expression of toxic proteins to tumor only. Luc, luciferase; LNP, lipid nanoparticle; miRt, microRNA target site.