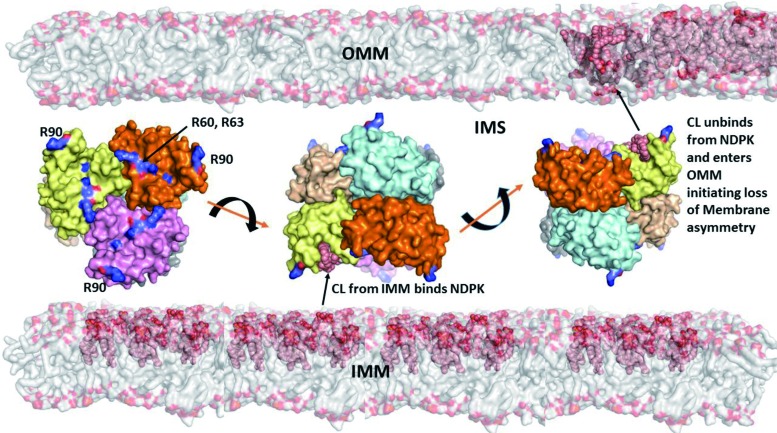
FIG. 4.
A model illustrating different stages of externalization of CL from the IMM to the OMM, including the CL transfer through the intermembrane space by NDPK-D. Hexameric complexes of NDPK-D consist of monomers colored in six different colors. Shown also are R90-containing sites involved in binding of CLs. Model of a bilayer made up of DOPC (shown as gray surface) and CL molecules are illustrated as pink spheres, with head-groups colored orange. The van-der-Waal's surface of hexameric protein NDPK is shown in the IMM at different positions. The conserved arginine residues implicated in binding of CL are labeled and highlighted in the leftmost hexamer (134). The asymmetry in the CL distribution in IMM and OMM is indicated by highlighting the CL, with its higher content in IMM versus OMM, before release of CL from the CL-NDPK complex (rightmost hexamer). NDPK-D, nucleoside-diphosphate kinase D; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine. To see this illustration in color, the reader is referred to the web version of this article at www.liebertpub.com/ars