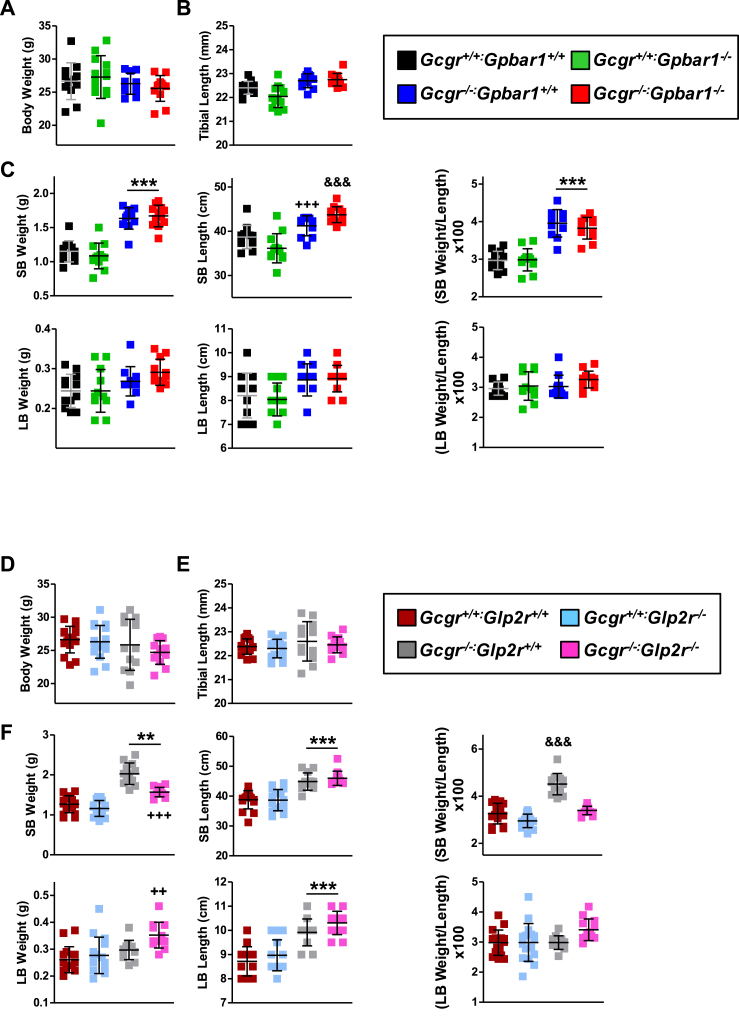
Figure 2.
Body weight (A & D), tibial length (B & E) and intestinal biometry (C & F) in Gcgr−/−:Gpbar1−/−(A–C) and Gcgr−/−:Glp2r−/−(D–F) double knockout mice and their single knockout and wild-type littermates. Body weight was assessed following overnight fasting 1 week before take down which was performed under random-fed conditions. Shown are individual data points with overlapping mean ± SD (n = 11–16 mice per genotype, combined from 2 independent mouse cohorts). SB: small bowel, LB: large bowel. Panel C: ***p < 0.001 Gcgr−/−:Gpbar1+/+ & Gcgr−/−:Gpbar1−/− vs Gcgr+/+:Gpbar1+/+ & Gcgr+/+:Gpbar1−/−; +++p < 0.001 Gcgr−/−:Gpbar1+/+ vs Gcgr+/+:Gpbar1−/−; &&&p < 0.001 Gcgr−/−:Gpbar1−/− vs Gcgr+/+:Gpbar1+/+ & Gcgr+/+:Gpbar1−/−. Panel F: **p < 0.01 & ***p < 0.001 Gcgr−/−:Glp2r+/+ & Gcgr−/−:Glp2r−/− vs Gcgr+/+:Glp2r+/+ & Gcgr+/+:Glp2r−/−; ++p < 0.01 Gcgr−/−:Glp2r−/− vs Gcgr+/+:Glp2r+/+ & Gcgr+/+:Glp2r−/−; +++p < 0.001 Gcgr−/−:Glp2r−/− vs Gcgr−/−:Glp2r+/+; &&&p < 0.001 Gcgr−/−:Glp2r+/+ vs Gcgr+/+:Glp2r+/+, Gcgr+/+:Glp2r−/− & Gcgr−/−:Glp2r−/−. Statistical significance was assessed by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's multiple comparison post hoc test.