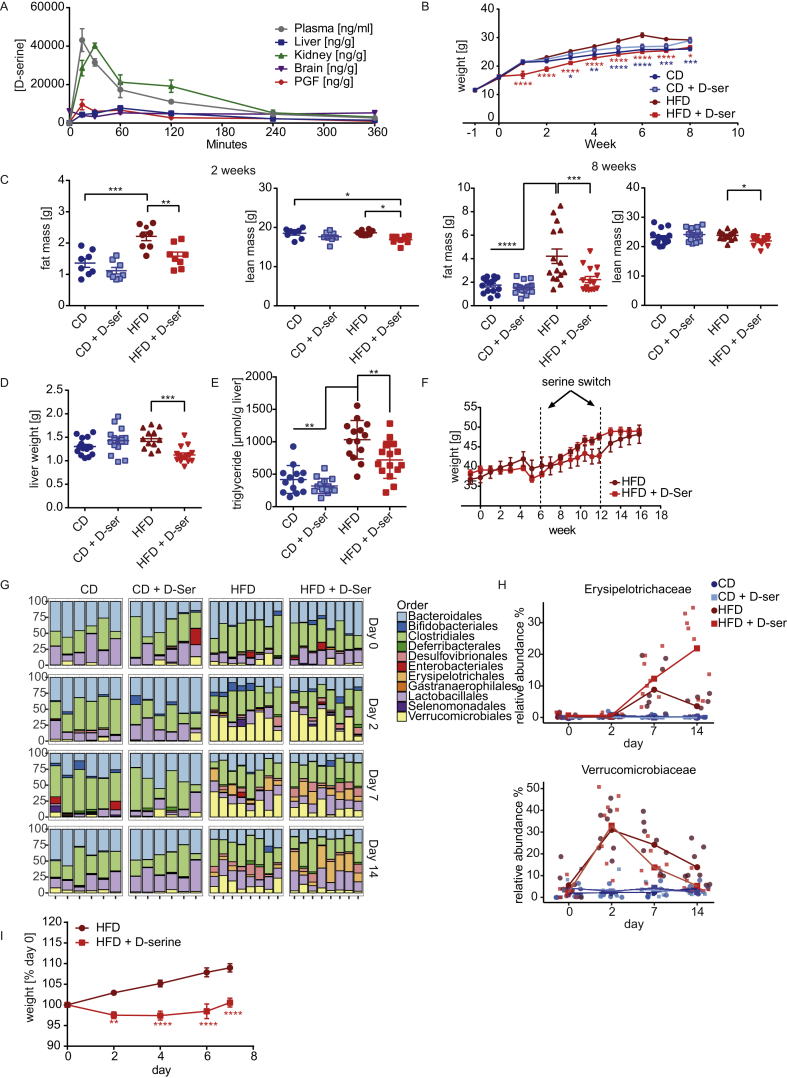
Figure 1.
d-serine regulates food preference and HFD induced weight gain. (A) 8 week old C57Bl/6 mice were gavaged with 100 mg d-serine/kg body weight or saline as controls. Mice gavaged with saline were used as controls and shown as time 0. Groups of four mice gavaged with d-serine were sacrificed after 15, 30, 60, 120, 240, and 360 min after administration and d-serine concentrations were measured by mass spectrometry. (B) Body weight curves of 4 week old C57Bl/6 mice fed a CD or HFD, and drinking water supplemented with or without 10 g/l d-serine throughout 8 weeks (n = 7–8). (C) Body composition after 2 and 8 weeks of serine supplementation (n = 7–16). (D) Liver weights after 8 weeks of treatment (n = 15–16). (E) Liver triglyceride content after 8 weeks of d-serine supplementation (n = 15–16). (F) Weight gain during 15 weeks of serine supplementation after 7 weeks on HFD (n = 4). After 6 and 12 weeks, the water bottles were switched. (G) Relative microbiota abundance at order level. The bar plot is displayed by treatment and day of intervention (n = 6–8). (H) Relative abundance dynamics of bacterial biomarkers Erysipelotrichaceae and Verrucomicrobiaceae (Akkermansia). (I) Weight gain in germfree C57Bl/6 mice fed with HFD with or without 1% d-serine supplementation (n = 5). Data are shown as mean ± SEM. Statistics were calculated either by one-way or two-way ANOVA with Tukey's or Sidak's (for germfree mice) multiple comparison post-hoc test (****P < 0.0001, ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05).