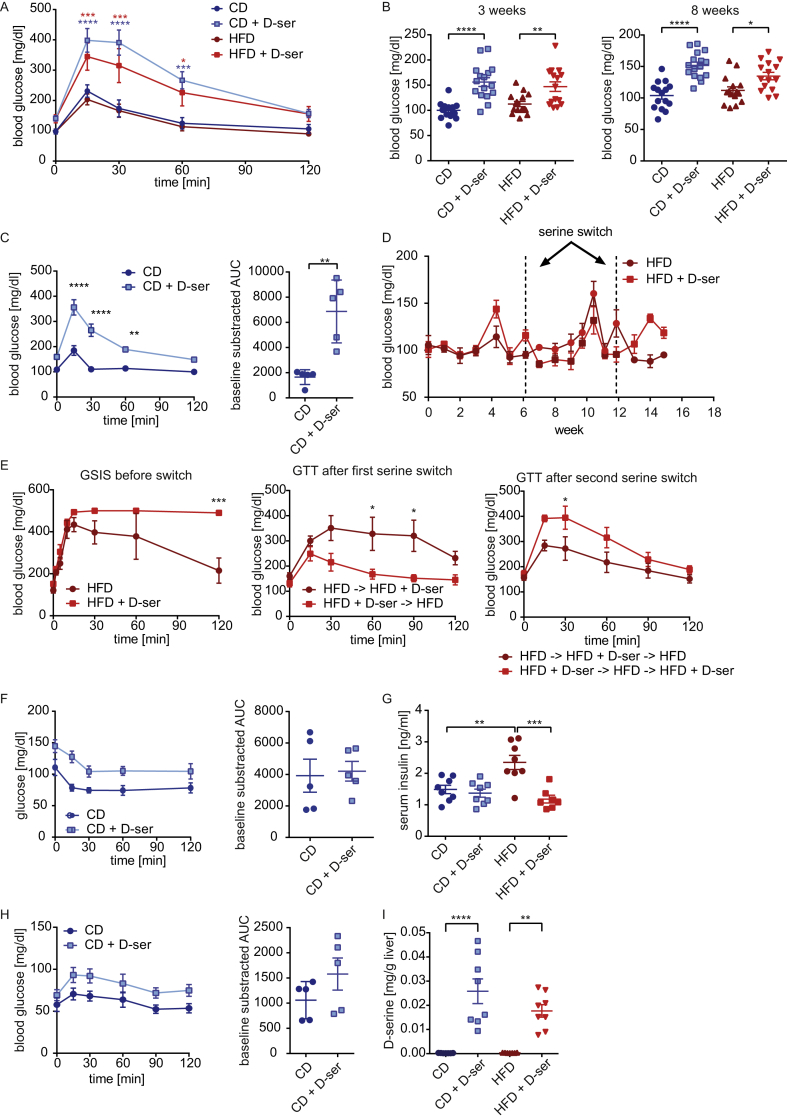
Figure 2.
d-serine supplementation impairs glucose but not insulin tolerance. (A) ipGTT after 6 weeks of d-serine supplementation (n = 7–8). (B) Blood glucose levels after three (random fed) and eight (4 h fasted) weeks of d-serine supplementation (n = 15–16). (C) ipGTT after 2 weeks of d-serine supplementation (n = 5). (D) Random fed blood glucose levels during 15 weeks of d-serine supplementation following 8 weeks on HFD prior to d-serine supplementation (n = 4). At weeks 6 and 12, d-serine supplementation was switched. (E) ipGTT after 5 weeks of d-serine supplementation, 6 weeks after the first serine switch and 3 weeks after the second serine switch of the mice shown in (D). (F) Insulin tolerance test after 3 weeks of d-serine supplementation (n = 5). (G) Random fed serum insulin levels after 3 weeks of d-serine supplementation. (H) ipPTT after 5 weeks of d-serine supplementation (n = 5). (I) Liver d-serine levels after 8 weeks chronic d-serine supplementation (n = 7–8). Data are shown as mean ± SEM. Statistics were calculated either by t-test, one-way or two-way ANOVA with Tukey's or Sidaks (for Fig 2C and E, F, H) multiple comparison post-hoc test (****P < 0.0001, ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05).