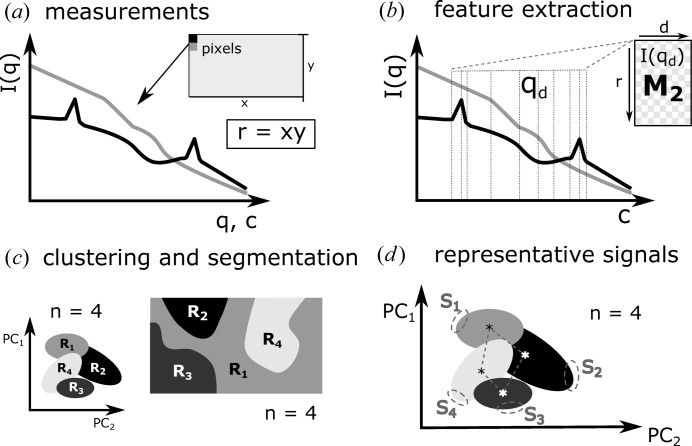
Figure 3.
Scheme of the data analysis procedure. (a) Collection of azimuthally integrated SAXS/WAXS intensity curves 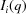 , for
, for 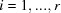 , where r is the number of
, where r is the number of 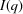 points. (b) M
2 is formed by selecting only the d intensities
points. (b) M
2 is formed by selecting only the d intensities 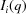 where inflection points occur. (c) Dimensionality reduction: principal component analysis is applied to M
2 and the number of main variables is reduced to m principal components PCj, for
where inflection points occur. (c) Dimensionality reduction: principal component analysis is applied to M
2 and the number of main variables is reduced to m principal components PCj, for 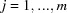 . The optimal number of clusters n is evaluated and the signals are classified into n clusters. We assume n = 4 in this example. The scanned map is segmented according to the clustering results. (d) Estimation of a representative signal
. The optimal number of clusters n is evaluated and the signals are classified into n clusters. We assume n = 4 in this example. The scanned map is segmented according to the clustering results. (d) Estimation of a representative signal 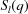 by selecting points that are located furthest from all centroids, for
by selecting points that are located furthest from all centroids, for  . Further details about each step can be found in the text.
. Further details about each step can be found in the text.