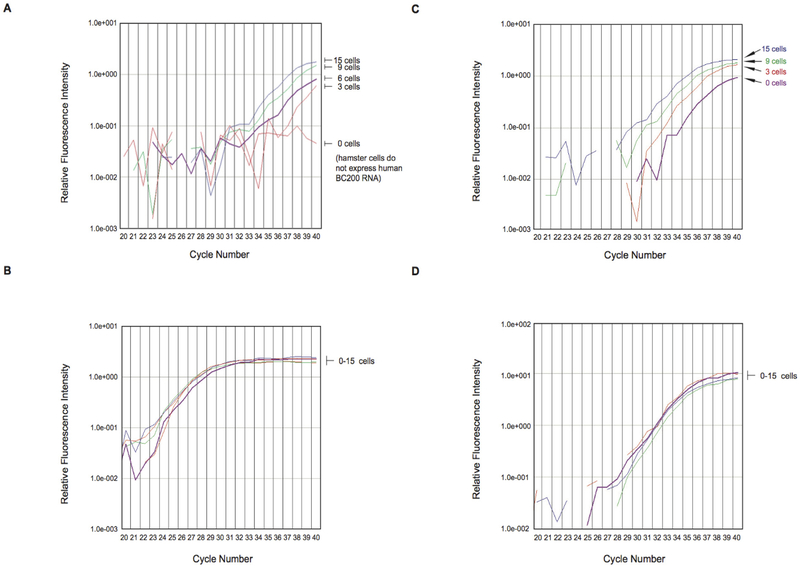
Figure 4.
(A and B) Limiting dilution experiments with MCF-7 breast cancer cell RNA in Baby Hamster Kidney (BHK) cell RNA (A) The panel shows qtr.-PCR amplification plots for BC200 RNA Total RNA isolated from MCF-7 cells, representing the respective number of cells indicated, was diluted with total RNA from 104 BHK cells and subjected to qtr.-PCR amplification The curves show that BC200 RNA amplification allowed detection of as few as three MCF-7 cells The zero MCF-7 cells sample failed to reach amplification threshold after 40 cycles, indicating that no BC200 RNA was detected (B) Control amplification experiments were performed with acidic ribosomal protein (ARP) mRNA In contrast to BC200 amplification, ARP amplification resulted in plots that were grouped together, indicating constant expression levels independent of MCF-7 cell numbers (C and D) Limiting dilution experiments: MCF-7 breast cancer cell RNA in RNA from blood of healthy subjects (C) The panel shows qtr.-PCR amplification plots for BC200 RNA Total RNA isolated from MCF-7 cells (from 3 to 15 cells) was diluted with total RNA (10 ng) from blood of healthy human subjects BC200 RNA qtr.-PCR amplification allowed detection of three MCF-7 cells (D) Control amplification experiments were performed with GAPDH mRNA As in the experiments with ARP mRNA, GAPDH amplification plots were grouped together.