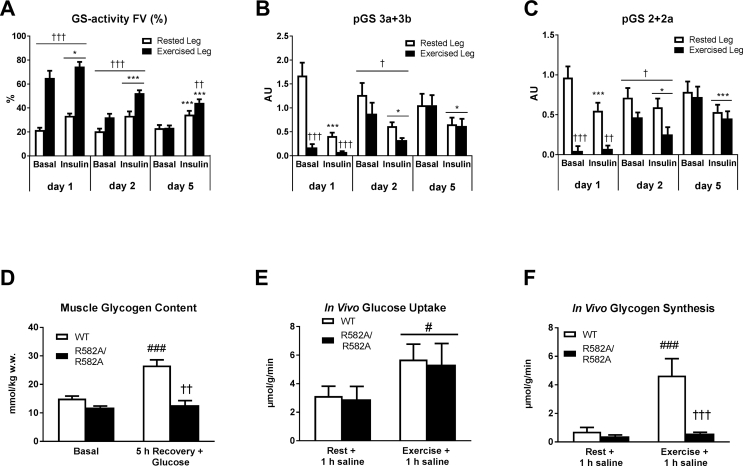
Figure 5.
Muscle glycogen supercompensation in man reveals sustained activation of glycogen synthase (GS) far beyond normalized muscle glycogen content. Enzyme-activity of GS was determined in muscle homogenates as fractional activity (activity in the presence of 0.17 mM G6P relative to 8 mM G6P) (A). GS phosphorylation at the key regulatory sites 3a+3 b and 2+2a was measured by immunoblotting (B–C). Glycogen content in quadriceps muscle from mice expressing a G6P-insensitive form of GS in muscle (R582A/R582A) was measured under basal conditions (Basal) and 5 h following exercise where glucose gavage (2 g/kg body wt) was given immediately and 1 h post exercise (D). In vivo glucose uptake (E) and in vivo glycogen synthesis (F) in quadriceps muscle from WT and R582A/R582A mice was determined in the rested state (Rest + 1 h saline) and prior exercised state (Exercise + 1 h saline) by oral gavage of saline containing [14C]- Glucose and [3H]-2-deoxyglucose. Data are expressed as means ± SEM (n = 8–9 for A–C and n = 6–8 for D–E). ∗p ≤ 0.01 and ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001 for effect of insulin infusion/time. (†) p ≤ 0.1, †p ≤ 0.05, ††p ≤ 0.01 and †††p ≤ 0.001 for effect of leg in human experiment and for effect of genotype in mice experiment. #p ≤ 0.05 and ###p ≤ for significantly different from corresponding resting value. Main effect is indicated by horizontal line.