Figure 1.
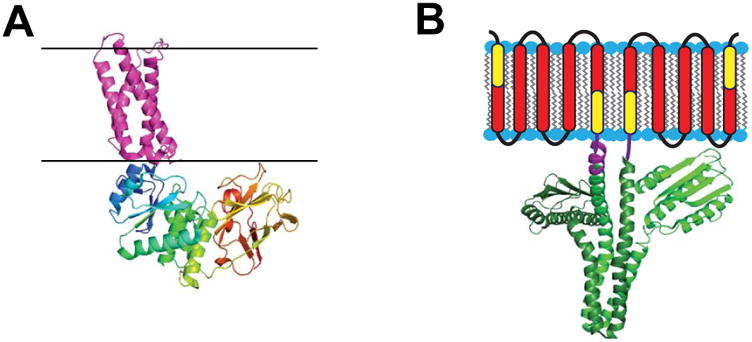
Enzymes for which water soluble catalytic domains are coupled to integral membrane sensor regulatory domains. A) Crystal structure of the voltage-sensor domain of the Ci-VSP phosphatase (4G80) [59] in purple juxtaposed to its cytosolic domain (3AWF) [154] with multicolored chains. Black lines indicate expected membrane boundaries. This figure is adapted from [58]. B) The DesK temperature sensor protein homodimer, with the transmembrane region represented in cartoon form and the cytosolic domain depicted as based on its crystal structure (3GIG) [155], which is that of a non-symmetric dimer. It has been shown that the indicated yellow components of the first and last DesK monomer transmembrane segments can be fused to create a temperature-sensing-functional single pass protein referred to as MS-DesK [78,80]. The linker between the transmembrane and cytosolic domain in each monomer is represented in purple (the crystallographically resolved segment of this linker is longer in the subunit on the left than in the subunit on the right). This figure is adapted from [76].
