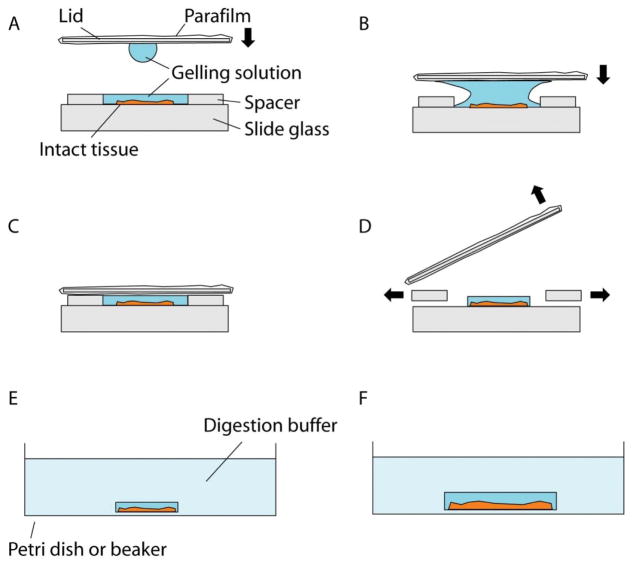
Figure 4.
Gelation of intact tissues. (A) Schematic showing the side view of a gelation chamber. The intact tissue is placed in between the spacers, which should be thicker than the tissue. The lid is moved towards the chamber, bearing a droplet of the gelling solution. (B) Schematic showing lid placement. The lid is moved towards the sample so that the droplet merges with the gelling solution in the chamber, which prevents air pocket formation in the gel. (C) Schematic showing the gelation chamber ready for polymerization at 37°C. After the chamber is correctly constructed and filled with gelling solution, polymerization is carried out at 37°C for 2 hours. (D) Schematic showing removal of the lid and the spacers. The lid is first pried open and then the gel is trimmed with a razor blade. (E) Schematic showing the digestion step. The trimmed gel is placed in the digestion buffer. (F) Schematic showing the gel slightly expanded after the digestion step.