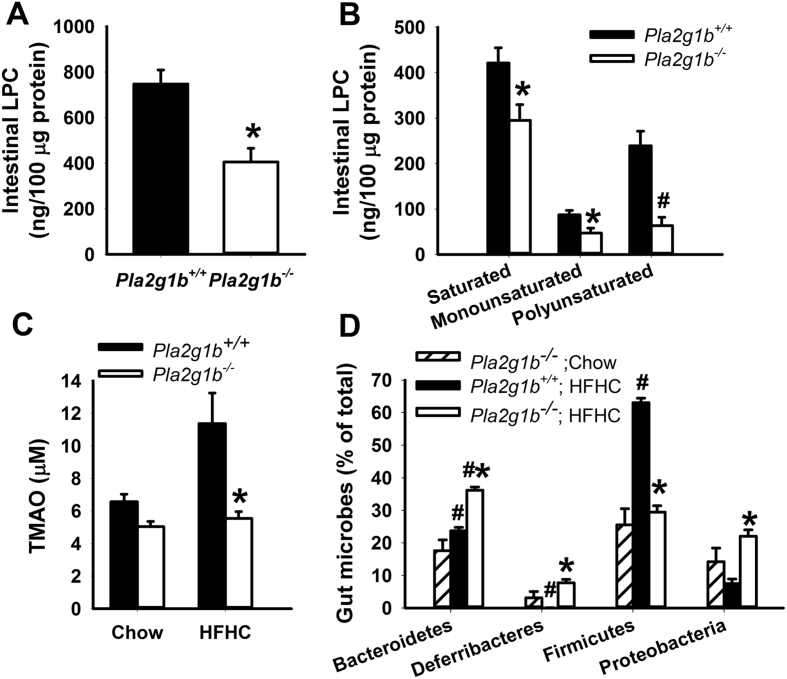
Figure 2.
Influence of PLA2G1B gene inactivation on intestinal LPC and plasma TMAO levels and gut microbiota in C57BL/6J mice. (A) Intestinal LPC levels in HFHC-fed Pla2g1b+/+ and Pla2g1b−/− mice (N = 6 in each group). (B) Levels of saturated, monounsaturated, and polyunsaturated LPC in intestine of Pla2g1b+/+ (filled bars) and Pla2g1b−/− (open bars) mice. (C) Plasma TMAO levels in chow-fed Pla2g1b+/+ mice (N = 6), and Pla2g1b−/− mice (N = 5), HFHC-fed Pla2g1b+/+ (N = 10), and HFHC-fed Pla2g1b−/− (N = 5) mice. Data from Pla2g1b+/+ mice are shown in filled bars and Pla2g1b−/− mice are shown in open bars. (D) Distribution of major bacterial phyla in the cecum of chow-fed Pla2g1b−/− mice (striped bars, N = 3) and HFHC-fed Pla2g1b+/+ (filled bars, N = 6) and HFHC-fed Pla2g1b−/− (open bars, N = 6) mice. Data are presented as mean ± s.e.m. *P < 0.01 by t test compared to wild type mice on same diet; #P < 0.001 compared to mice with same genotype on chow diet.