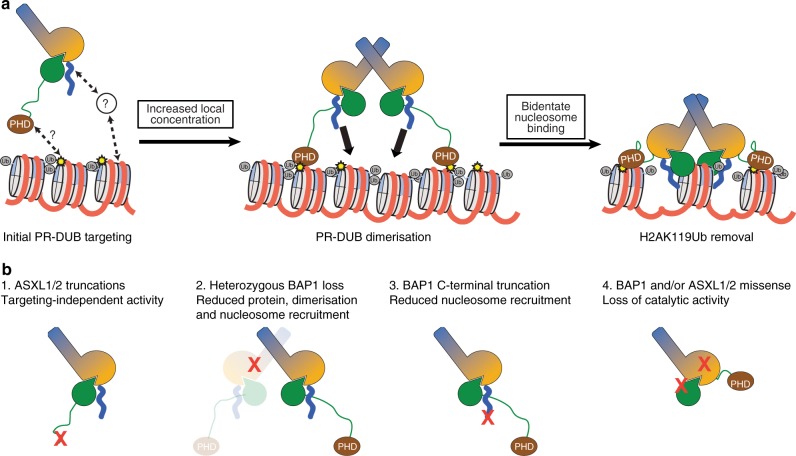
Fig. 7.
Model for PR-DUB regulation and its disruption in human cancers. a The 1:1 PR-DUB complex is first targeted to nucleosomal arrays either via the PHD domain of ASX-like proteins or through interactions with transcription factors and/or other binding partners (left). Enrichment of multiple 1:1 complexes in specific genomic regions increases the local PR-DUB concentration, favouring Calypso/BAP1 dimerisation and formation of a bidentate PR-DUB complex (middle). With bidentate complex formation, two C-terminal positively charged tails of Calypso/BAP1 are optimally oriented, enhancing nucleosome recruitment and efficient removal of H2AK119Ub (right). b Distinct classes of human PR-DUB mutations can impair PR-DUB targeting, recruitment, and activity on nucleosomes via multiple mechanisms