Fig. 2.
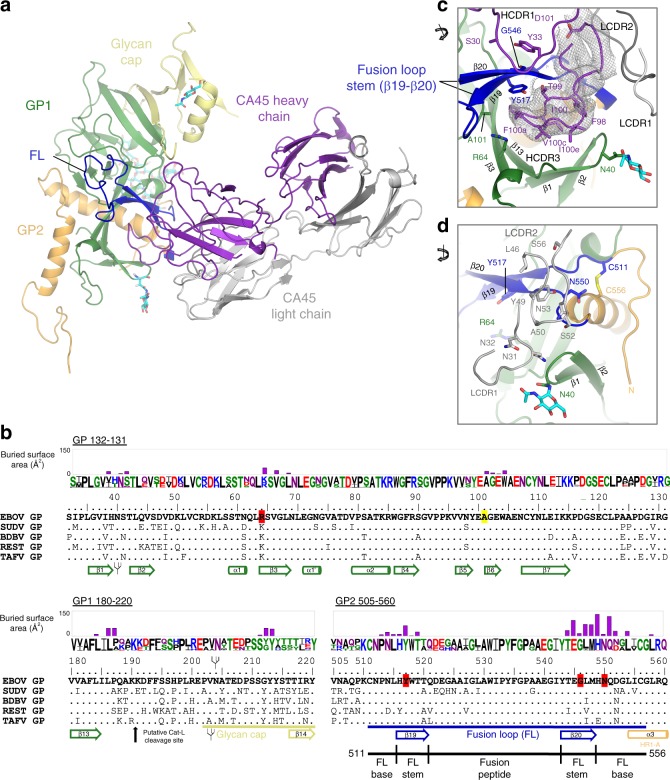
CA45-EBOV GP interactions. a Single protomer of EBOV GPΔMuc bound to CA45 Fab, colored as in Fig. 1. b Sequence alignment of representative sequences of the five ebolavirus species at selected regions of GP. Buried surface areas on GP residues at the CA45-binding interface are plotted for each residue of the epitope. Residues of EBOV GP that ablate CA45 recognition upon alanine mutation or those associated with viral escape are highlighted in red and yellow, respectively. Sequence logo reflects sequence variation across representative ebolavirus sequences from previous outbreaks35, with residues colored by amino acid type. GP subdomains, secondary structure elements, and N-linked glycosylation sequon sites are annotated below the sequence alignment. c Close-up view of CA45 interactions with fusion loop stem. Residues sensitive to alanine mutation and viral escape are shown in stick representation on GP along with select interacting CA45 residues. 2fofc composite omit electron density contoured at 1σ is shown for the HDCR3 in gray. d Close-up view of light chain interactions with fusion loop base