Figure 2.
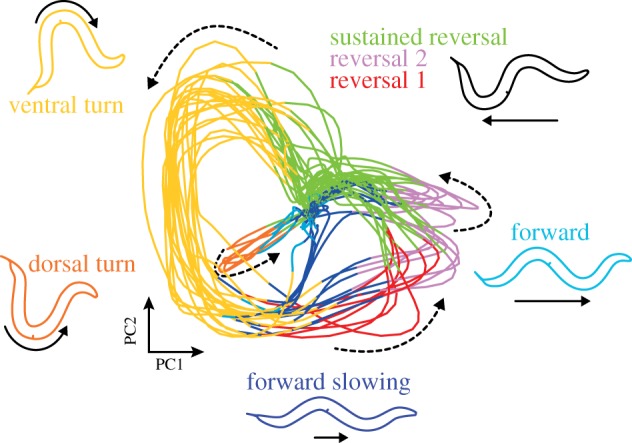
Phase plot of the first two principal components (PCs) of an 18 min long C. elegans brain-wide calcium imaging dataset from Kato et al. [20]. Activity of a subset of neurons with known motor output allows classification of brain state into different motor command states: forward, forward slowing, three reversal states, as well as ventral and dorsal turns (see [20]). These brain states are colour-coded, and schematics of the movements are shown. The brain state is continuously changing; the direction of brain state time evolution is shown by dashed arrows. Note that the manifold assembles individual behavioural commands into the major action sequence of the worm; moreover, discrete transitions between behavioural command states are embedded in a smooth progression of brain state.
