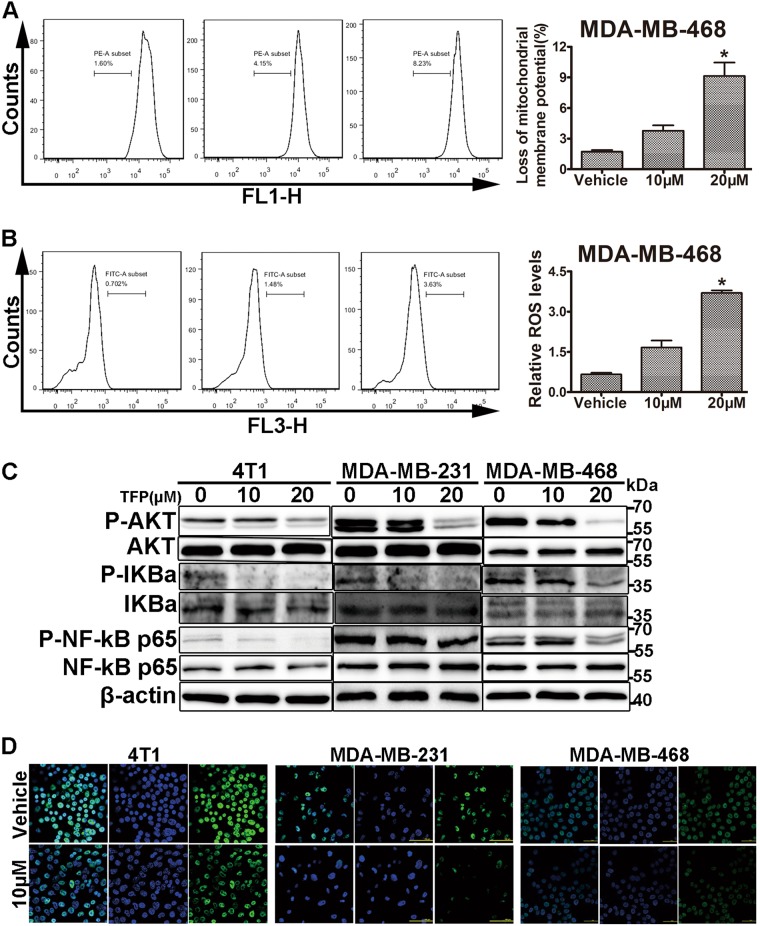
Fig. 4. TFP induced mitochondria-mediated apoptosis of TNBC cells.
a TFP treatment decreased mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm) in MDA-MB-468 cells. Cells were treated with various concentrations of TFP for 24 h and then stained with Rh123 to measure the change of ΔΨm by flow cytometry. Quantified values are shown on the right (*P < 0.05); the treatment group and the control group were compared by t test. b TFP increased ROS level in MDA-MB-468 cells. After treatment with various concentrations of TFP for 12 h, MDA-MB-468 cells were incubated with DCFH-DA and then ROS levels were measured by DCF fluorescence with flow cytometry. Quantified values were shown on the right (*P < 0.05). c The expression of related proteins was determined by western blotting. 4T1, MDA-MB-231, and MDA-MB-468 cells were treated with TFP for 72 h and the expression of P-AKT, AKT, P-IKBa, IKBa, P-NF-kB p65, and NF-kB p65 were detected. β-actin served as internal control. d TFP inhibited the NF-kB p65 nuclear translocation. The intracellular localization of NF-kB p65 was determined by immunofluorescence. Pictures were taken with a laser-scanning confocal microscopy (Nikon). Scale bars represent 50 μm