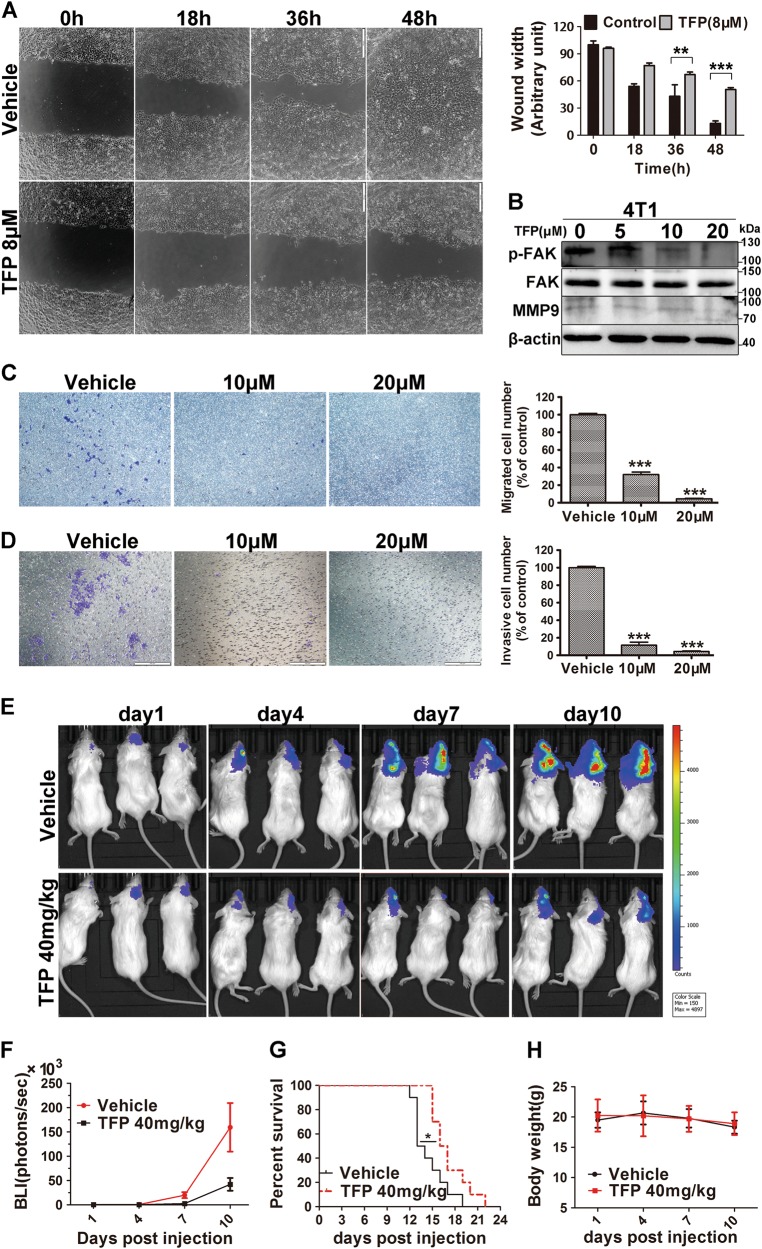
Fig. 6. TFP’s inhibitory effects on brain metastasis of TNBC in intracarotid model.
a TFP inhibited wound healing of 4T1 cells. Quantified values were shown on the right. The width of the wound was measured manually (**P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001); the treatment group and the control group were compared by t test. b The expression of proteins important for migration and invasion were detected by western blot after TFP treatment in 4T1 cells. β-actin served as the loading control. c TFP inhibited the migration of 4T1 cell in the transwell migration assay. 4T1 cells were exposed to TFP for 18 h. The quantified values were shown in right (***P < 0.001). d TFP inhibited the invasion of 4T1 cell in the transwell invasion assay. 4T1 cells were exposed to TFP for 24 h. The quantified values were shown on the right (***P < 0.001). e, f TFP inhibits the growth of 4T1 brain metastasis in intracarotid model in vivo. The metastasis growth in the brain was monitored by noninvasive bioluminescence imaging technology (IVIS, PerkinElmer) in vivo every 3 days. The imaging was captured at the peak time after i.p. injection of 150 mg/kg d-luciferin. The imaging exposure time was 60 s. f The tumor burden was measured and judged by bioluminescence intensity (BLI). g TFP treatment prolongs the survival of mice bearing brain metastasis. The survival of the mice bearing brain metastasis was monitored everyday during the treatment (*P < 0.05). h Body weight changes of mice bearing brain metastasis during TFP treatment. The results showed that TFP treatment did not cause obvious weight changes compared with vehicle-treated mice