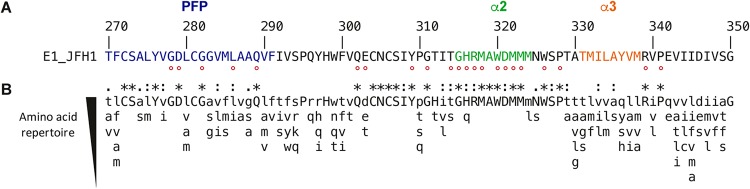
FIG 1.
E1 C-terminal region sequence analyses. (A) The E1 aa270-350 sequence from the HCV JFH1 strain (AB047639; genotype 2a) is indicated with respect to the polyprotein numbering. Amino acids mutated in this study are indicated by a red dot. (B) Amino acid repertoires of the C-terminal region of E1. The amino acid (aa) repertoire was deduced from the ClustalW multiple alignment of the 28 representative E1 sequences from confirmed genotypes and subtypes in the European HCV database (https://euhcvdb.ibcp.fr/euHCVdb/jsp/nomen_tab1.jsp). Amino acids observed at a given position in fewer than two distinct sequences were not included. Amino acids observed at a given position in more than 25 distinct sequences are shown in capital letters. The degree of amino acid conservation at each position can be inferred from the extent of variability (with the observed amino acids listed in decreasing order of frequency from top to bottom), together with the similarity index according to ClustalW convention (asterisk [*], invariant; colon [:], highly similar; dot [.], similar).