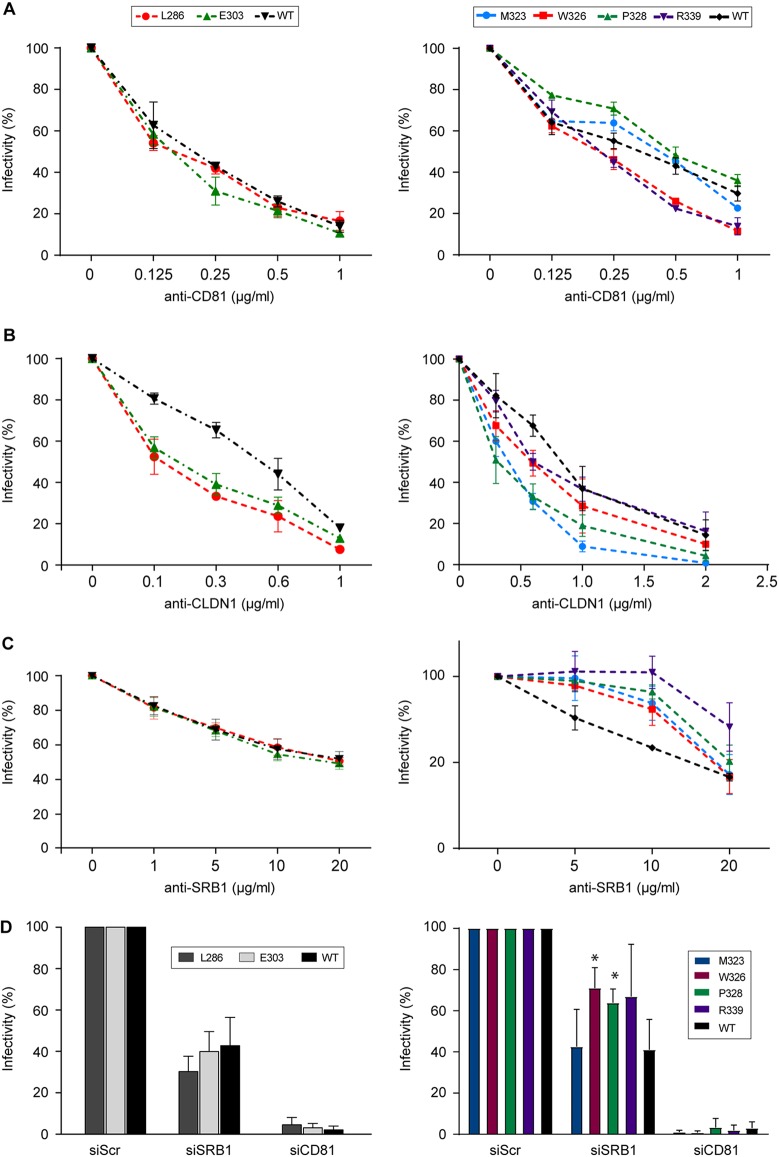
FIG 7.
Effect of E1 mutations on the recognition of HCV receptors. Huh-7 cells were preincubated at 37°C for 2 h with increasing concentrations of antibodies targeting HCV receptors: anti-CD81 MAb JS81 (A), anti-CLDN1 MAb OM8A9-A3 (B), and anti-SR-BI MAb Cla-I (C). E1 mutants or wild-type virus were then inoculated onto the cells. At 72 h postinfection, the residual infectivity was determined by immunofluorescence. The values are the combined data from three independent experiments. The error bars represent standard errors of the means. Results were compared to those of the wild type. A P value of <0.05 was determined for mutants L286A, E303A, M323A, and P328A in the presence of anti-CLDN1 MAbs and for mutants M323A, W326A, P328A, and R339A in the presence of anti-SR-BI MAbs. (D) SRB1 or CD81 expression was downregulated by siRNA targeting SRB1 or CD81 mRNA. Infectivity is expressed as the percentage of infection performed in the presence of the control siRNA. Mean values and standard deviations from three independent experiments are shown. The unpaired t test was used to compare the infectivities of the wild-type and mutant viruses. Differences were considered statistically significant if the P value was <0.05.